Page 516 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 516
472 section iii Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` pathology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` dERmatology
Neuromuscular junction diseases
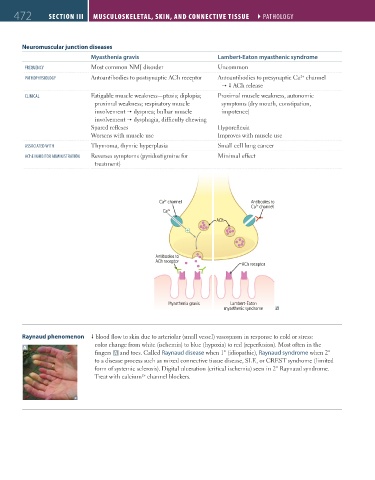
Myasthenia gravis Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
FREQUEnCy Most common NMJ disorder Uncommon
2+
pathophysiology Autoantibodies to postsynaptic ACh receptor Autoantibodies to presynaptic Ca channel
ACh release
CliniCal Fatigable muscle weakness—ptosis; diplopia; Proximal muscle weakness, autonomic
proximal weakness; respiratory muscle symptoms (dry mouth, constipation,
involvement dyspnea; bulbar muscle impotence)
involvement dysphagia, difficulty chewing
Spared reflexes Hyporeflexia
Worsens with muscle use Improves with muscle use
assoCiatEd With Thymoma, thymic hyperplasia Small cell lung cancer
aChE inhiBitoR administRation Reverses symptoms (pyridostigmine for Minimal effect
treatment)
Ca channel Antibodies to
2+
Ca channel
2+
Ca
2+
ACh
Antibodies to
ACh receptor
ACh receptor
Myasthenia gravis Lambert-Eaton
myasthenic syndrome
Raynaud phenomenon blood flow to skin due to arteriolar (small vessel) vasospasm in response to cold or stress:
color change from white (ischemia) to blue (hypoxia) to red (reperfusion). Most often in the
A
fingers A and toes. Called Raynaud disease when 1° (idiopathic), Raynaud syndrome when 2°
to a disease process such as mixed connective tissue disease, SLE, or CREST syndrome (limited
form of systemic sclerosis). Digital ulceration (critical ischemia) seen in 2° Raynaud syndrome.
2+
Treat with calcium channel blockers.
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 472 11/7/19 5:23 PM