Page 540 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 540
496 SecTioN iii Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology
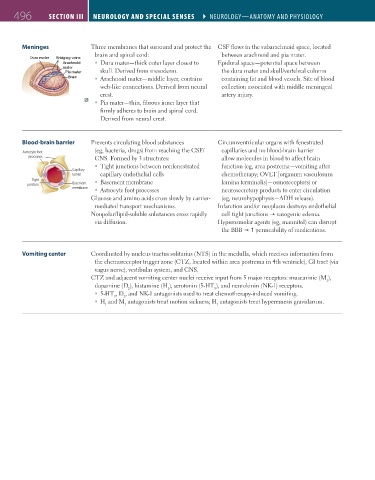
Meninges Three membranes that surround and protect the CSF flows in the subarachnoid space, located
brain and spinal cord: between arachnoid and pia mater.
Bi
Bridging ve
Bridging veins vgggg
Bridging veinsdidigggg
Bridging vein
i
Bridging
Bridging veins
Du
D Du Bi i s
Dura materuruuururuurraararaaaraaa maa mma m tm ttmatermmmatermatermmater
Ara
Arachnoid ddidddoidoononhhchccccc Dura mater—thick outer layer closest to Epidural space—potential space between
A A Arac
Arac
mater ereeteata
m
Pi P Pia mater rrreetetaamammmaaia skull. Derived from mesoderm. the dura mater and skull/vertebral column
B B B Brainnniniara Arachnoid mater—middle layer, contains containing fat and blood vessels. Site of blood
web-like connections. Derived from neural collection associated with middle meningeal
crest. artery injury.
Pia mater—thin, fibrous inner layer that
firmly adheres to brain and spinal cord.
Derived from neural crest.
Blood-brain barrier Prevents circulating blood substances Circumventricular organs with fenestrated
(eg, bacteria, drugs) from reaching the CSF/ capillaries and no blood-brain barrier
Astrocyte foot
processes CNS. Formed by 3 structures: allow molecules in blood to affect brain
Tight junctions between nonfenestrated function (eg, area postrema—vomiting after
Capillary
lumen capillary endothelial cells chemotherapy; OVLT [organum vasculosum
Tight Basement membrane lamina terminalis]—osmoreceptors) or
junction Basement
membrane
Astrocyte foot processes neurosecretory products to enter circulation
Glucose and amino acids cross slowly by carrier- (eg, neurohypophysis—ADH release).
mediated transport mechanisms. Infarction and/or neoplasm destroys endothelial
Nonpolar/lipid-soluble substances cross rapidly cell tight junctions vasogenic edema.
via diffusion. Hyperosmolar agents (eg, mannitol) can disrupt
the BBB permeability of medications.
Vomiting center Coordinated by nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in the medulla, which receives information from
the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ, located within area postrema in 4th ventricle), GI tract (via
vagus nerve), vestibular system, and CNS.
CTZ and adjacent vomiting center nuclei receive input from 5 major receptors: muscarinic (M ),
1
dopamine (D ), histamine (H ), serotonin (5-HT ), and neurokinin (NK-1) receptors.
2
1
3
5-HT , D , and NK-1 antagonists used to treat chemotherapy-induced vomiting.
3
2
H and M antagonists treat motion sickness; H antagonists treat hyperemesis gravidarum.
1 1 1
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 496 11/8/19 7:39 AM