Page 630 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 630
586 SeCTIOn III Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy
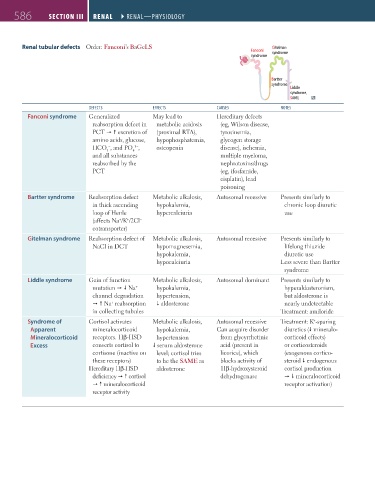
Renal tubular defects Order: Fanconi’s BaGeLS Gitelman
Fanconi syndrome
syndrome
Bartter
syndrome
Liddle
syndrome,
SAME
DEFECts EFFECts CAUsEs NotEs
Fanconi syndrome Generalized May lead to Hereditary defects
reabsorption defect in metabolic acidosis (eg, Wilson disease,
PCT excretion of (proximal RTA), tyrosinemia,
amino acids, glucose, hypophosphatemia, glycogen storage
HCO , and PO , osteopenia disease), ischemia,
3–
–
4
3
and all substances multiple myeloma,
reabsorbed by the nephrotoxins/drugs
PCT (eg, ifosfamide,
cisplatin), lead
poisoning
Bartter syndrome Reabsorption defect Metabolic alkalosis, Autosomal recessive Presents similarly to
in thick ascending hypokalemia, chronic loop diuretic
loop of Henle hypercalciuria use
(affects Na /K /2Cl
+
–
+
cotransporter)
Gitelman syndrome Reabsorption defect of Metabolic alkalosis, Autosomal recessive Presents similarly to
NaCl in DCT hypomagnesemia, lifelong thiazide
hypokalemia, diuretic use
hypocalciuria Less severe than Bartter
syndrome
Liddle syndrome Gain of function Metabolic alkalosis, Autosomal dominant Presents similarly to
mutation Na hypokalemia, hyperaldosteronism,
+
channel degradation hypertension, but aldosterone is
Na reabsorption aldosterone nearly undetectable
+
in collecting tubules Treatment: amiloride
Syndrome of Cortisol activates Metabolic alkalosis, Autosomal recessive Treatment: K -sparing
+
Apparent mineralocorticoid hypokalemia, Can acquire disorder diuretics ( mineralo-
Mineralocorticoid receptors. 11β-HSD hypertension from glycyrrhetinic corticoid effects)
Excess converts cortisol to serum aldosterone acid (present in or corticosteroids
cortisone (inactive on level; cortisol tries licorice), which (exogenous cortico-
these receptors) to be the SAME as blocks activity of steroid endogenous
Hereditary 11β-HSD aldosterone 11β-hydroxysteroid cortisol production
deficiency cortisol dehydrogenase mineralocorticoid
mineralocorticoid receptor activation)
receptor activity
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 586 11/7/19 5:42 PM