Page 650 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 650
606 SeCTIOn III Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy Renal ` RENAL—PhARmACoLogy
Nephroblastoma Also called Wilms tumor. Most common renal malignancy of early childhood (ages 2–4). Contains
embryonic glomerular structures. Presents with large, palpable, unilateral flank mass A and/or
A
hematuria and possible HTN.
“Loss of function” mutations of tumor suppressor genes WT1 or WT2 on chromosome 11.
May be a part of several syndromes:
WAGR complex—Wilms tumor, Aniridia (absence of iris), Genitourinary malformations,
mental Retardation/intellectual disability (WT1 deletion)
Denys-Drash syndrome—Wilms tumor, Diffuse mesangial sclerosis (early-onset nephrotic
syndrome), Dysgenesis of gonads (male pseudohermaphroditism), WT1 mutation
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome—Wilms tumor, macroglossia, organomegaly,
hemihyperplasia (WT2 mutation), omphalocele
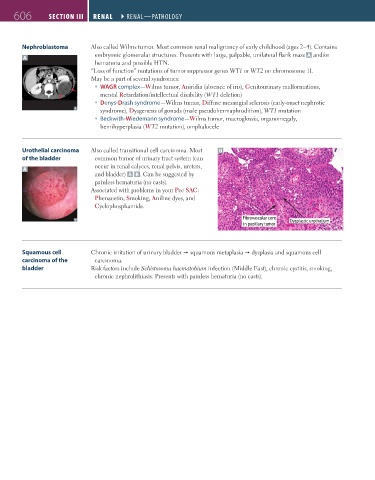
Urothelial carcinoma Also called transitional cell carcinoma. Most B
of the bladder common tumor of urinary tract system (can
occur in renal calyces, renal pelvis, ureters,
A
and bladder) A B . Can be suggested by
painless hematuria (no casts).
Associated with problems in your Pee SAC:
Phenacetin, Smoking, Aniline dyes, and
Cyclophosphamide.
Fibrovascular core Dysplastic urothelium
in papillary tumor
Squamous cell Chronic irritation of urinary bladder squamous metaplasia dysplasia and squamous cell
carcinoma of the carcinoma.
bladder Risk factors include Schistosoma haematobium infection (Middle East), chronic cystitis, smoking,
chronic nephrolithiasis. Presents with painless hematuria (no casts).
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 606 11/7/19 5:42 PM