Page 649 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 649
Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy SeCTIOn III 605
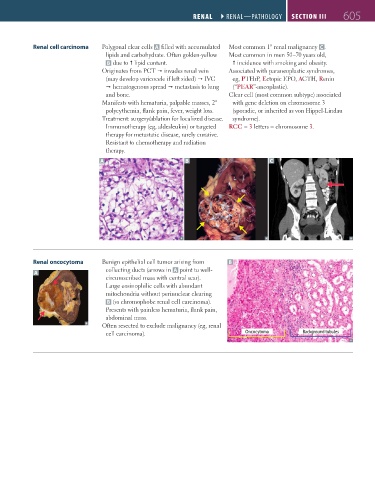
Renal cell carcinoma Polygonal clear cells A filled with accumulated Most common 1° renal malignancy C .
lipids and carbohydrate. Often golden-yellow Most common in men 50–70 years old,
B due to lipid content. incidence with smoking and obesity.
Originates from PCT invades renal vein Associated with paraneoplastic syndromes,
(may develop varicocele if left sided) IVC eg, PTHrP, Ectopic EPO, ACTH, Renin
hematogenous spread metastasis to lung (“PEAR”-aneoplastic).
and bone. Clear cell (most common subtype) associated
Manifests with hematuria, palpable masses, 2° with gene deletion on chromosome 3
polycythemia, flank pain, fever, weight loss. (sporadic, or inherited as von Hippel-Lindau
Treatment: surgery/ablation for localized disease. syndrome).
Immunotherapy (eg, aldesleukin) or targeted RCC = 3 letters = chromosome 3.
therapy for metastatic disease, rarely curative.
Resistant to chemotherapy and radiation
therapy.
A B C
Renal oncocytoma Benign epithelial cell tumor arising from B
collecting ducts (arrows in A point to well-
A
circumscribed mass with central scar).
Large eosinophilic cells with abundant
mitochondria without perinuclear clearing
B (vs chromophobe renal cell carcinoma).
Presents with painless hematuria, flank pain,
abdominal mass.
Often resected to exclude malignancy (eg, renal
cell carcinoma). Oncocytoma Background tubules
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 605 11/7/19 5:42 PM