Page 293 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 293
Chapter 5 Cold water systems
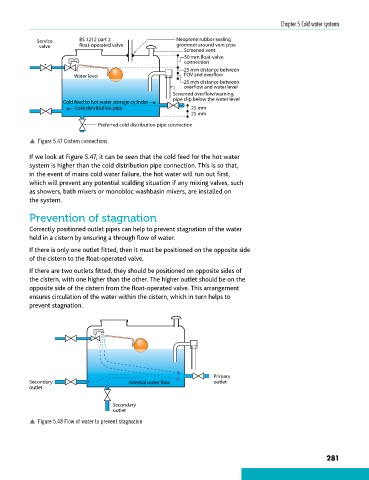
Service BS 1212 part 2 Neoprene rubber sealing
valve float-operated valve grommet around vent pipe
Screened vent
50 mm float-valve
connection
25 mm distance between
Water level FOV and overflow
25 mm distance between
overflow and water level
Screened overflow/warning
pipe clip below the water level
Cold feed to hot water storage cylinder
Cold distribution pipe 25 mm
25 mm
Preferred cold distribution pipe connection
p Figure 5.47 Cistern connections
If we look at Figure 5.47, it can be seen that the cold feed for the hot water
system is higher than the cold distribution pipe connection. This is so that,
in the event of mains cold water failure, the hot water will run out first,
which will prevent any potential scalding situation if any mixing valves, such
as showers, bath mixers or monobloc washbasin mixers, are installed on
the system.
Prevention of stagnation
Correctly positioned outlet pipes can help to prevent stagnation of the water
held in a cistern by ensuring a through flow of water.
If there is only one outlet fitted, then it must be positioned on the opposite side
of the cistern to the float-operated valve.
If there are two outlets fitted, they should be positioned on opposite sides of
the cistern, with one higher than the other. The higher outlet should be on the
opposite side of the cistern from the float-operated valve. This arrangement
ensures circulation of the water within the cistern, which in turn helps to
prevent stagnation.
Primary
Secondary Internal water flow outlet
outlet
Secondary
outlet
p Figure 5.48 Flow of water to prevent stagnation
281
9781510416482.indb 281 29/03/19 8:57 PM