Page 260 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 260
230 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
99.99---.---...- ...... �.,..,.--.,.........,.--,-,....,-i��---,�...,......, ... O.Ql
(o,., 0.05
99.9 .. l!>;z. 0.1
99.8 "-,/�� 'JC), 0.2
C),C'/, 0.5
99.0 o,,& 1.0
95.0 5.0
90.0 10.0 '*'
ii'
20.0 c: .,
·.;
..
i:
50.0 c:
.2
t,
�
0
20.0 o
10.0 90.0
5.0 95.0
1.0 99.0
0.5
0.2
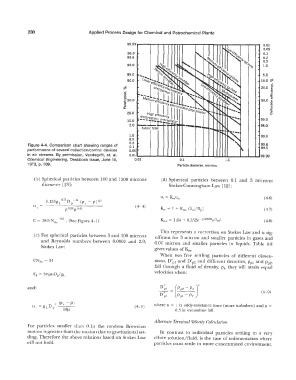
Figure 4-4. Comparison chart showing ranges of 0.1 99.8
99.9
periormance of several collection/control devices 0.05
in air streams. By permission, Vandegrift, et. al. O.Ql ..__ ..... _.._..._.._.....,.w.. __ _.._.._..._..._A,.., ..... ..._ ..._ _ _. 99.99
Chemical Engineering, Deskbook Issue, June 18, 0.01 0.1 1.0
1973, p. 1 09. Particle diameter, microns
(b) Spherical particles between 100 and 1500 microns (d) Spherical particles between 0.1 and 3 microns:
diameter [BJ: Stokes-Cunningham Law [12]:
u. = .K,,,urs (4-6)
o.J53g/·710/14 (p, - p)o.1
l1 l = (4-4)
p 0.29µ 0.43 (4-7)
-06
C = 18.5 NRc · , (See Figure 4-1) (4-8)
This represents a correction on Stokes Law and is sig-
(c) For spherical particles between 3 and 100 microns nificant for 3 micron and smaller particles in gases and
and Reynolds numbers between 0.0001 and 2.0, 0.01 micron and smaller particles in liquids. Table 4-8
Stokes Law: gives values of K,,,.
When two free settling particles of different climen-
CNRe = 24 sions, D' pl and D' P 2 and different densities, Ppl and Pp2,
fall through a fluid of density, Pr, they will attain equal
velocities when:
and:
(4-9)
(4-5) where n = 1 in eddy-resistance zone (more turbulent) and n =
0.5 in streamline fall.
Alternate Terminal Velocity Calculation
for particles smaller than 0.1µ the random Brownian
motion is greater than the motion due to gravitational set- In contrast to individual particles settling in a very
tling. Therefore the above relations based on Stokes Law dilute solution/fluid, is the case of sedimentation where
will not hold. particles must settle in more concentrated environment,