Page 370 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 370
338 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
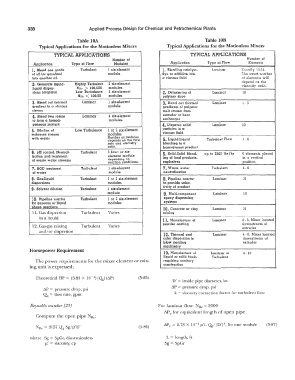
Table IOA Table IOB
Typical Applications for the Motionless Mixers Typical Applications for the Motionless Mixers
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
Number of Number of
Application Type of Flow Modules Application Type of Flow Elements
1. Blend one grade Turbulent 1 six-element 1. Blending catalyst. Laminar Usually 10-14.
of oil (or gasoline) module dye or additive into The exact number
Into another oil. a viscous fluid of elements will
depend on the
2. Generate liquid- Highly Turbulent 2 six-element viscosity ratio.
liquid disper- NRe > 100.000 modules
sions (droplets) Low Turbulence 3 six-element 2. De!ustering of Laminar 10
NRe < 100,00 modules polymer dope
3, Blend out thermal Laminar 1 six-element 3. Blend out thermal Laminar 4-6
gradient in a viscous module gradients of polymer
stream melt stream from
4, Blend two resins Laminar 4 six-element extruder or heat
to form a homoq- modules exchanger
geneous mixture 4. Disperse solid Laminar 10
5, Dilution of Low Turbulence l or 2 six-element particles in a
molasses stream modules viscous fluid
with water Number of modules 5. Liquid-Liquid Turbulent Flow 4-6
depends on the flow
rate and viscosity blending to a
ratio. homogenous product
6, pH control. Neutral- Turbulent 1 four- or six- 6. Solid-Solid Blend- up to 2500 lbs/hr 6 elements placed
izalion and treatment element module ing of food products, in a vertical
of waste water streams depending on explosives position.
reaction conditions.
7, BOD treabnent Turbulent 1 six-element 7. Waste water Turbulent 4-6
of water module neutralization
8. Gas-liquid Turbulent 1 or 2 six-element 8. Pipeline reactor Laminar 10
dispersions modules lo provide selec-
tivity of product
9, Solvent dilution Turbulent l six-element
module 9. Multi-component Laminar 10
l Q. Pipeline reactor Turbulent I or 2 six-element epoxy dispensing
for gaseous or liquid modules systems
phase reactions 10. Concrete or clay Laminar 10
11. Gas dispersion Turbulent Varies mixing
in a liquid
11. Manufacture of Laminar 4 - 6. Mixer located
powder coating downstream ol
12. Gas-gas mixing Turbulent Varies extruder
and/ or dispersion
12. Thermal and Laminar 4 - 6. Mixer located
color dispersion in downstream ol
blow molding extruder
machinery
Horsepower Requirement
13. Manufacture ol Laminar or 4-10
liquid or solid foods Turbulent
The power requirements for the mixer element or mix- requiring sanitary
construction
ing unit is expressed:
Theoretical HP= (5.83 X 10- 4) (Qg) (t.P) (5-85)
D' = inside pipe diameter, in.
t.P = pressure drop, psi
t.P = pressure drop, psi
Qg = flow rate, gpm k = viscosity correction factor for turbulent flow
Reynolds number [25} For laminar flow: NRc < 2000
L'1P for equivalent length of open pipe
0
Compute the open pipe NRe:
NRc = 3157 Qg Sg/µ'D' (5-86) t.P 0 = 2.73 X 10- 4 µ'L Qg/(D')1. for one module (5-87)
where Sg = SpGr, dimensionless L = length, ft
µ' = viscosity, cp Sg = SpGr