Page 669 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 669
Appendix 617
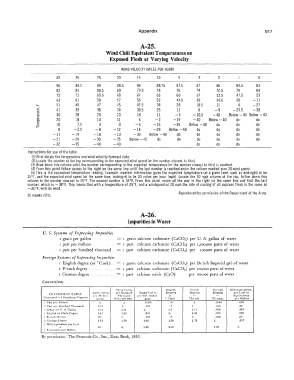
A-25.
Wind Chill Equivalent Temperatures on
Exposed Flesh at Varying Velocity
WIND VELOCITY (MILES PER HOUR)
45 35 25 20 15 10 5 3 2 0
90 89.5 89 88.5 88 88.75 87.5 87 86 84.5 83
82 81 80.5 80 79.5 78 76 74 72.5 70 60
72 71 69.5 68 67 65 60 57 53.5 47.5 23
63 61 59 57 55 52 44.5 39 34.5 20 -11
...... 51 49 47 45 42.5 38 28 18.5 11 0 -27
Q) 41 39 36 34 30.5 25 11 0 -9 -23.5 -38
E
"' a, 30 28 25 23 18 11 -5 -16.5 -40 Below -40 Below -40
c. 20 18 14 11 6 -2 -19 -40 Below -40 do do
E
Q) 10 7.5 3 0 -6 -15 -35 Below -40 do do do
I-
0 -2.5 -8 -12 -18 --29 Below -40 do do do do
-11 -14 --18 -23 -30 Below -40 do do do do do
-21 -24 --30 -35 Below -40 do do do do do do
-32 -35 --40 -40 do do do
instructions for use of the table:
(1) First obtain the temperature and wind velocity forecast data.
(2) Locate the number at the top corresponding to the expected wind speed (or the number closest to this).
(3) Read down this column until the number corresponding to the expected temperature (or the number closest to this) is reached.
(4) From this point follow across to the right on the same line until the last number is reached under the column marked zero (0) wind speed.
(5) This is the equivalent temperature reading. Example: weather information gives the expected temperature (at a given time, such as midnight) to be
35°F, and the expected wind speed (at the same time, midnight) to be 20 miles per hour (mph). Locate the 20 mph column at the top, follow down this
column to the number nearest to 35°F. The nearest number is 34°F. From this point, move all the way to the right on the same line and find the last
number, which is - 38°F. This means that with a temperature of 35°F, and a windspeed of 20 mph the rate of cooling of all exposed flesh is the same as
- 38°F, with no wind.
Reproduced by permission of the Department of the Army.
do means ditto.
A-26.
Impurities in Water
U. S. Systems of Expressing Impurities
I grain per gallon I grain calcium carbonate (CaCO,) per U. S. gallon of water
I part per million I part calcium carbonate (CaCO,) per 1,000,000 pans of water
I part per hundred thousand I part calcium carbonate (CaCO,) per 100,000 parts of water
Foreign Systems of Expressing Impurities
I English degree (or "Clark) I grain calcium carbonate (CaCO,) per British Imperial gal. of water
I French degree . I part calcium carbonate (CaCO,) per 100,000 parts of water
I German degree I part calcium oxide (CaO) per roo.ooo parts of water
Conversions
l'arL"' CaCo, Jo:nKlish Jo"r,•nch Gnman Milli-equivelente
per Liter or
Grain� CAro1
CONVEllSION TAIILF: l'tHl:-4 ('a(:01 Jirr llundrrd pn (J.S. Gallon Dr>Krr<"s Df'l{tPl'R Dr�rees F,quivaJ,.nt..a
Thousand
or
(Jo:xpn·�"l,.fi 1n :I �ii,:-nifif'ant FiKUrt•!'I) rwr �fillion (l'l!'l./100,flOO) (�p5!") O Clark 0 1' rf'nrh ac.,,rman pt-r Million
[ppm)
0
1 l'art JH'i" Million I. .1 .07 .I .O!i60 .020
1 Part. JJN Hundred Thousand JO.O I. .7 I. .�60 .20
I �rain pN U. S. Gallon 17.1 I. 71 I. J.2 t.71 .958 .343
1 Enzl i rh or Clark Degree 14.3 1.(3 .RU I. I.43 .ROO .286
1 Frr-nr-h Or,.:rN'! 10. I. .ssn .7 !. .5�0 .20
l Grrman n,'l,!rN� 17.9 I. 79 I.04 1.24 l. 79 I. _357
"' so. 6. 2.92 3.60 2.80 J.
1 l-:quivalrnt pr-r Millinn
By permission, The Perrnutit Co., Inc., Data Book, 1953.