Page 670 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 670
618 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
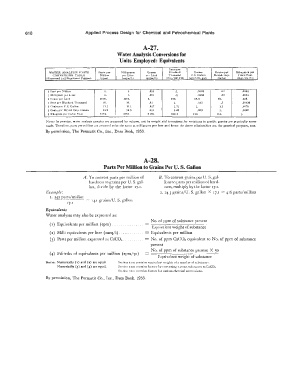
A-27.
Water Analysis Conversions for
Units Employed: Equivalents
J·ans per
WATER ANALYSIS IJNITS J>H.rl�" per MilligrarnR Grams llundr••d Gr11in!t Gralna per Kilof{rainfl per
CONVf:l\slON TAIILf; Million pN Li!N tu-r Lit er Thousand U.S. Gallon Hritiah Imp. Cubic Foot
( �"<prf'"l!'lr.:..l ta 3 �i9;nilirant Figurr!') (f,pml (m�m/1,) (grm!t L) (Pts./100,000) (•rs/U.S. gal) Gallon (Kgr/C'U. fl.)
I Part per Million i. 1. .001 .i .O!iR3 .07 .0004
1 Milli,:ram pr-r Liter 1. 1. .001 .1 .0583 .07 .0004
I Gram Jwr Liter 1000. 1000. 1. 100. !;JL3 70. .436
1 Part. pr-r J Iundred 'I'housend 10. 10. .OJ J. .583 • 7 .00436
I Grain ,,rr u.s. Gall•m 17.1 17.1 .017 1.71 1. 1.2 .1107�
I Grain prr Brili!'!h lmp. Gallon 1,.a 14.a .01·1 1.43 .K33 1. .0062
1 Kilr>Krain 1wr Cuhic F'nnt �:!lH. 2'l!hl. 2.291 229.4 134. 161. 1.
NoTE: In practice, water a nal ysis samples arc measured by volume. not by weight and corrections for variations ln·specific gravity are practically never
made. Therefore, parts per million ar e ;1�,umrcl to be the sarne as milligrams per luer anti hence the above relationships arc, for practical purposes, true.
By permission, The Permutit Co., Inc., Data Book, !953.
A-28.
Parts Per Million to Grains Per U. S. Gallon
A. To convert parts per million of B. To convert grains per U.S. gal-
hardness to grains per U.S. gal- lons to parts per million of hard-
lon, divide by the factor 17.r. ness, multiply by the factor 17.1.
Example: 2. 24.3 grains/U. S. gallon X 17.1 416 parts/million
1. 242 fl_�t.�/millior.
17.r q.1 grains/U. S. gallon
EqujvaJenls
Water analyses may also be expressed as:
No. of ppm of substance present
(1) Equivalents per million (epm)
Equivalent weight of substance
(2) Milli equivalents per liter (meq/1) .. Equivalents per million
(3) Parts per million expressed as CaCO,. No. of ppm CaCO. equivalent to No. of ppm of substance
present
No. of ppm of substance present X 50
(4) Fiftieths of equivalents per million (epm/xo)
Equivalent weight of substance
Nons: Numerically (1) and (2) arc equal. SC'c1i11n )C:<111 contains equivalent wciuhts of :1 numbc r of .o;11h..i:1nC'C'�.
Numerically (3) and (4) arc equal. Section :,cx111 contnins Iactors for converting various suhvtunces to CaC0 1 •
Section x x u t contains factors for various chemical conversions.
By permission, The Permutit Co., Inc., Data Book, 1953.