Page 93 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 93
Fluid Flow 77
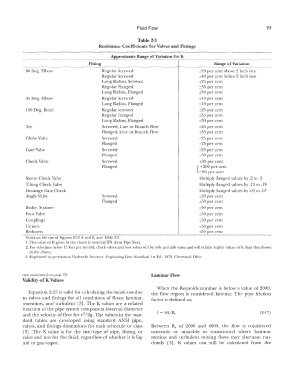
Table 2-3
Resistance Coefficients for Valves and Fittings
==� - -==-------- - ----
Approximate Range of Variation for K
----------
Fitting Range of Variation
---- -----------------�--------------------+----------�
90 Deg. Elbow Regular Screwed ±20 per cent above 2 inch size
Regular Screwed ±40 per cent below 2 inch size
Long Radius, Screwed ±25 per cent
Regular Flanged ±35 per cent
Long Radius, Flanged ±30 per cent
45 Deg. Elbow Regular Screwed ±10 per cent
Long Radius, Flanged ±10 per cent
180 Deg. Bend Regular screwed ±25 per cent
Regular Flanged ±35 per cent
Long Radius, Flanged ±30 per cent
Tee Screwed, Line or Branch Flow ±25 per cent
Flanged, Line or Branch Flow ±35 per cent
Globe Valve Screwed ±25 per cent
Flanged ±25 per cent
Gate Valve Screwed ±25 per cent
Flanged ±50 per cent
Check Valve Screwed ±30 per cent
Flanged { + 200 per cent
-80 per cent
Sleeve Check Valve Multiply flanged values by .2 to .5
Tilting Check Valve Multiply flanged values by .13 LO .19
Drainage Gate Check Multiply flanged values by _03 to .07
Angle Valve Screwed ±20 per cent
Flanged ±50 per cent
Basket Strainer ±50 per cent
Foot Valve ±50 per cent
Couplings ±50 per cent
Unions ±50 per cent
Reducers �=�c===e''e="'e'--�=e---====-============��=-==±-50 per cent _
Notes on the use of Figlires 2-12 A. and B, and Table�-- -----
1. The value of D given in the char ls is nominal !PS (Iron Pipe Size).
2. For velocities below 15 feet per second, check valves and foot valves will be only partially open and will exhibit higher values of K than that shown
in the charts,
3_ Reprinted by permission Hydraulic Institute, Engineering Data Handbook, I st Ed., 1979, Cleveland, Ohio.
(text continued from page 72j Laminar Flow
Validity of K Values
'When the Reynolds number is below a value of 2000,
Equation 2-25 is valid for calculating the head loss clue the flow region is considered laminar. The pipe friction
to valves and fittings for all conditions of flows: laminar, factor is defined as:
transition, and turbulent [3]. The K values are a related
function of the pipe system component internal diameter
and the velocity of flow for v /2g. The values in the stan- f = 64/R,, (2-17)
2
dard tables are developed using standard Al'\/SI pipe,
valves, and fittings dimensions for each schedule or class Between Re of 2000 and 4000, the flow is considered
[3]. The K value is for the sizez'type of pipe, fitting, or unsteady or unstable or transitional where laminar
valve and not for the fluid, regardless of whether it is liq- motion and turbulent mixing flows may alternate ran-
uid or gas/vapor. domly [3]. K values can still be calculated from the