Page 170 - Template Tesis UTM v2.0
P. 170
7
6
Specific impact energy (J.dm 3 /kg) 4
5
3
2
1
0
G2/B3/G2 G2/J3/G2 G2/F3/G2
S3
S2
S1
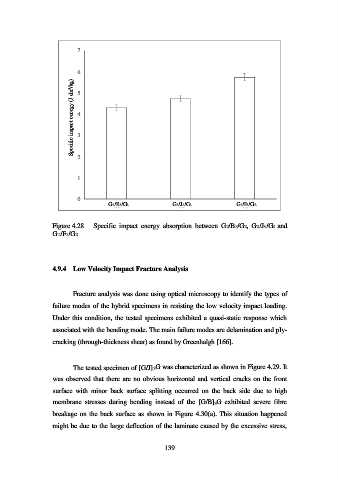
Figure 4.28 Specific impact energy absorption between G2/B3/G2, G2/J3/G2 and
G2/F3/G2
4.9.4 Low Velocity Impact Fracture Analysis
Fracture analysis was done using optical microscopy to identify the types of
failure modes of the hybrid specimens in resisting the low velocity impact loading.
Under this condition, the tested specimens exhibited a quasi-static response which
associated with the bending mode. The main failure modes are delamination and ply-
cracking (through-thickness shear) as found by Greenhalgh [166].
The tested specimen of [G/J]3G was characterized as shown in Figure 4.29. It
was observed that there are no obvious horizontal and vertical cracks on the front
surface with minor back surface splitting occurred on the back side due to high
membrane stresses during bending instead of the [G/B]3G exhibited severe fibre
breakage on the back surface as shown in Figure 4.30(a). This situation happened
might be due to the large deflection of the laminate caused by the excessive stress,
139