Page 87 - Template Tesis UTM v2.0
P. 87
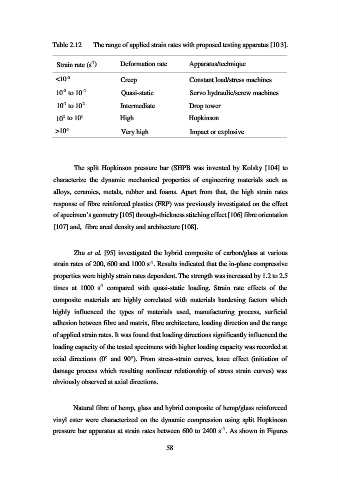
Table 2.12 The range of applied strain rates with proposed testing apparatus [103].
-1
Strain rate (s ) Deformation rate Apparatus/technique
-5
<10 Creep Constant load/stress machines
-1
-5
10 to 10 Quasi-static Servo hydraulic/screw machines
-1
2
10 to 10 Intermediate Drop tower
4
2
10 to 10 High Hopkinson
4
>10 Very high Impact or explosive
The split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB was invented by Kolsky [104] to
characterize the dynamic mechanical properties of engineering materials such as
alloys, ceramics, metals, rubber and foams. Apart from that, the high strain rates
response of fibre reinforced plastics (FRP) was previously investigated on the effect
of specimen’s geometry [105] through-thickness stitching effect [106] fibre orientation
[107] and, fibre areal density and architecture [108].
Zhu et al. [95] investigated the hybrid composite of carbon/glass at various
-1
strain rates of 200, 600 and 1000 s . Results indicated that the in-plane compressive
properties were highly strain rates dependent. The strength was increased by 1.2 to 2.5
-1
times at 1000 s compared with quasi-static loading. Strain rate effects of the
composite materials are highly correlated with materials hardening factors which
highly influenced the types of materials used, manufacturing process, surficial
adhesion between fibre and matrix, fibre architecture, loading direction and the range
of applied strain rates. It was found that loading directions significantly influenced the
loading capacity of the tested specimens with higher loading capacity was recorded at
axial directions (0° and 90°). From stress-strain curves, knee effect (initiation of
damage process which resulting nonlinear relationship of stress strain curves) was
obviously observed at axial directions.
Natural fibre of hemp, glass and hybrid composite of hemp/glass reinforcced
vinyl ester were characterized on the dynamic compression using split Hopkinosn
-1
pressure bar apparatus at strain rates between 600 to 2400 s . As shown in Figures
58