Page 90 - Template Tesis UTM v2.0
P. 90
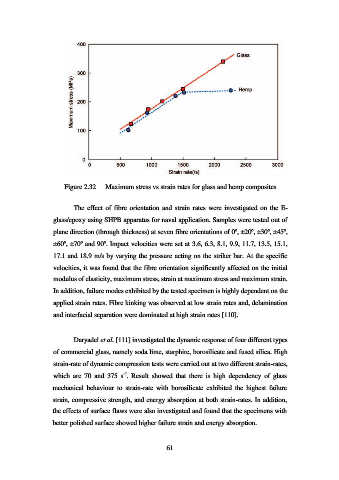
Figure 2.32 Maximum stress vs strain rates for glass and hemp composites
The effect of fibre orientation and strain rates were investigated on the E-
glass/epoxy using SHPB apparatus for naval application. Samples were tested out of
plane direction (through thickness) at seven fibre orientations of 0º, ±20º, ±30º, ±45º,
±60º, ±70º and 90º. Impact velocities were set at 3.6, 6.3, 8.1, 9.9, 11.7, 13.5, 15.1,
17.1 and 18.9 m/s by varying the pressure acting on the striker bar. At the specific
velocities, it was found that the fibre orientation significantly affected on the initial
modulus of elasticity, maximum stress, strain at maximum stress and maximum strain.
In addition, failure modes exhibited by the tested specimen is highly dependent on the
applied strain rates. Fibre kinking was observed at low strain rates and, delamination
and interfacial separation were dominated at high strain rates [110].
Daryadel et al. [111] investigated the dynamic response of four different types
of commercial glass, namely soda lime, starphire, borosilicate and fused silica. High
strain-rate of dynamic compression tests were carried out at two different strain-rates,
-1
which are 70 and 375 s . Result showed that there is high dependency of glass
mechanical behaviour to strain-rate with borosilicate exhibited the highest failure
strain, compressive strength, and energy absorption at both strain-rates. In addition,
the effects of surface flaws were also investigated and found that the specimens with
better polished surface showed higher failure strain and energy absorption.
61