Page 14 - Spotlight A+ Physics Form 4.5
P. 14
Form
5
Chapter 3 Electricity Physics
3.4
Aim: To investigate how the resistivity of a wire, ρ affects its resistance.
Problem statement: How the resistivity of a wire, ρ affects the resistance of the wire?
Hypothesis: Materials with high resistivity gives higher resistance.
Variables:
(a) Manipulated: Resistivity of wire, ρ
Discussions: ©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
(b) Responding: Resistance of wire, R
(c) Constant: Length of wire, temperature, cross-sectional area of wire
Apparatus and Materials:
50 cm constantan wire (s.w.g. 24), 50 cm copper wire (s.w.g. 24), 50 cm tungsten wire (s.w.g. 24), connecting
wires, three dry cells, switch, ammeter (0 – 1 A), voltmeter (0 – 5 V), rheostat and battery holder
Operational definition:
The resistance of the conductor, R, is given by the ratio of the reading of voltmeter to the reading of the CHAP
ammeter.
3
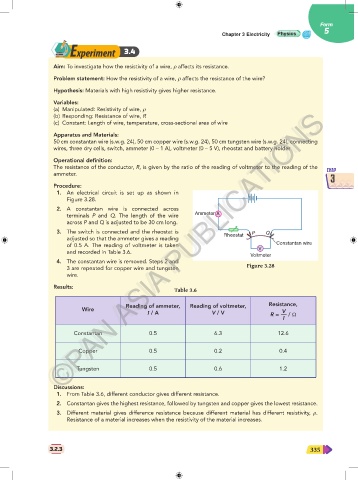
Procedure:
1. An electrical circuit is set up as shown in
Figure 3.28.
2. A constantan wire is connected across
Ammeter A
terminals P and Q. The length of the wire
across P and Q is adjusted to be 30 cm long.
3. The switch is connected and the rheostat is Rheostat P Q
adjusted so that the ammeter gives a reading
of 0.5 A. The reading of voltmeter is taken V Constantan wire
and recorded in Table 3.6.
Voltmeter
4. The constantan wire is removed. Steps 2 and Figure 3.28
3 are repeated for copper wire and tungsten
wire.
Results:
Table 3.6
Reading of ammeter, Reading of voltmeter, Resistance,
Wire V
I / A V / V R = — / Ω
I
Constantan 0.5 6.3 12.6
Copper 0.5 0.2 0.4
Tungsten 0.5 0.6 1.2
1. From Table 3.6, different conductor gives different resistance.
2. Constantan gives the highest resistance, followed by tungsten and copper gives the lowest resistance.
3. Different material gives difference resistance because different material has different resistivity, ρ.
Resistance of a material increases when the resistivity of the material increases.
3.2.3 335