Page 19 - Spotlight A+ Physics Form 4.5
P. 19
Form
4
Chapter 3 Gravitation Physics
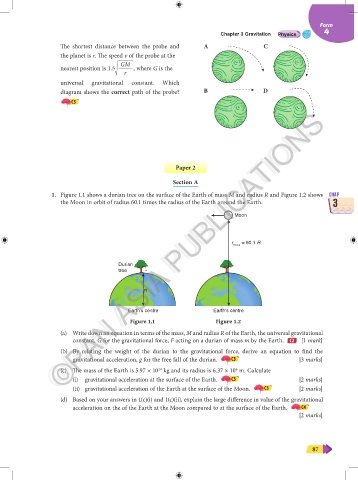
The shortest distance between the probe and A C
the planet is r. The speed v of the probe at the
GM
nearest position is 1.5 , where G is the
r
universal gravitational constant. Which
diagram shows the correct path of the probe? B D
C3
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Paper 2
Section A
1. Figure 1.1 shows a durian tree on the surface of the Earth of mass M and radius R and Figure 1.2 shows CHAP
the Moon in orbit of radius 60.1 times the radius of the Earth around the Earth. 3
Moon
r = 60.1 R
moon
Durian
tree
R
Earth’s centre Earth’s centre
Figure 1.1 Figure 1.2
(a) Write down an equation in terms of the mass, M and radius R of the Earth, the universal gravitational
constant, G for the gravitational force, F acting on a durian of mass m by the Earth. C2 [1 mark]
(b) By relating the weight of the durian to the gravitational force, derive an equation to find the
gravitational acceleration, g for the free fall of the durian. C3 [3 marks]
(c) The mass of the Earth is 5.97 × 10 kg and its radius is 6.37 × 10 m. Calculate
24
6
(i) gravitational acceleration at the surface of the Earth. C3 [2 marks]
(ii) gravitational acceleration of the Earth at the surface of the Moon. C3 [2 marks]
(d) Based on your answers in 1(c)(i) and 1(c)(ii), explain the large difference in value of the gravitational
acceleration on the of the Earth at the Moon compared to at the surface of the Earth. C4
[2 marks]
87