Page 18 - Spotlight A+ Physics Form 4.5
P. 18
Form
5
Chapter 2 Pressure Physics
SPM Clone
5. Figure 5 shows a boy floating at the surface of The speed of flow of water will increase if the
water. container is tilted in the direction shown because
C3
A the surface area of the water increases
B the volume of air in the container increases
C the tap is nearer to the floor
D the tap is at a deeper level below the water
surface
CHAP
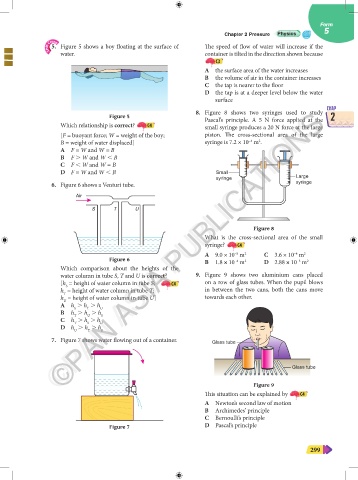
8. Figure 8 shows two syringes used to study
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Figure 5 Pascal’s principle. A 5 N force applied at the 2
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Which relationship is correct? C4 small syringe produces a 20 N force at the large
[F = buoyant force; W = weight of the boy; piston. The cross-sectional area of the large
2
–4
B = weight of water displaced] syringe is 7.2 × 10 m .
A F = W and W = B
B F . W and W , B
C F , W and W = B
D F = W and W , B Small
syringe Large
6. Figure 6 shows a Venturi tube. syringe
Air
S T U
Figure 8
What is the cross-sectional area of the small
syringe? C4
A 9.0 × 10 m C 3.6 × 10 m 2
2
–5
–4
Figure 6 B 1.8 × 10 m D 2.88 × 10 m 2
–3
2
–4
Which comparison about the heights of the
water column in tube S, T and U is correct? 9. Figure 9 shows two aluminium cans placed
[h = height of water column in tube S; C4 on a row of glass tubes. When the pupil blows
S
h = height of water column in tube T; in between the two cans, both the cans move
T
h = height of water column in tube U] towards each other.
U
A h . h . h U
S
T
B h . h . h S
U
T
C h . h . h U
T
S
D h . h . h
U T S
7. Figure 7 shows water flowing out of a container. Glass tube
Glass tube
Figure 9
This situation can be explained by C4
A Newton’s second law of motion
B Archimedes’ principle
C Bernoulli’s principle
Figure 7 D Pascal’s principle
299