Page 15 - 1202 Question Bank Chemistry Form 4 KSSM
P. 15
5 Chemical Bonds
Chapter
NOTES
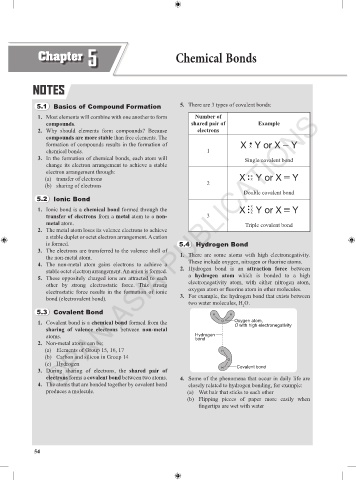
5.1 Basics of Compound Formation 5. There are 3 types of covalent bonds:
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
1. Most elements will combine with one another to form Number of
compounds. shared pair of Example
2. Why should elements form compounds? Because electrons
compounds are more stable than free elements. The
formation of compounds results in the formation of X X Y or X Y
chemical bonds. 1
3. In the formation of chemical bonds, each atom will Single covalent bond
change its electron arrangement to achieve a stable
electron arrangement through:
(a) transfer of electrons X X Y or X Y
X
(b) sharing of electrons 2
Double covalent bond
5.2 Ionic Bond
X
1. Ionic bond is a chemical bond formed through the X X Y or X Y
X
transfer of electrons from a metal atom to a non- 3
metal atom. Triple covalent bond
2. The metal atom loses its valence electrons to achieve
a stable duplet or octet electron arrangement. A cation
is formed. 5.4 Hydrogen Bond
3. The electrons are transferred to the valence shell of
the non-metal atom. 1. There are some atoms with high electronegativity.
4. The non-metal atom gains electrons to achieve a These include oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine atoms.
stable octet electron arrangement. An anion is formed. 2. Hydrogen bond is an attraction force between
5. These oppositely charged ions are attracted to each a hydrogen atom which is bonded to a high
other by strong electrostatic force. This strong electronegativity atom, with either nitrogen atom,
electrostatic force results in the formation of ionic oxygen atom or fluorine atom in other molecules.
bond (electrovalent bond). 3. For example, the hydrogen bond that exists between
two water molecules, H O.
2
5.3 Covalent Bond H H
1. Covalent bond is a chemical bond formed from the O Oxygen atom,
O with high electronegativity
sharing of valence electrons between non-metal
atoms. Hydrogen
2. Non-metal atoms can be: bond
(a) Elements of Group 15, 16, 17 H
(b) Carbon and silicon in Group 14 O
(c) Hydrogen
3. During sharing of electrons, the shared pair of H Covalent bond
electrons forms a covalent bond between two atoms. 4. Some of the phenomena that occur in daily life are
4. The atoms that are bonded together by covalent bond closely related to hydrogen bonding, for example:
produces a molecule. (a) Wet hair that sticks to each other
(b) Flipping pieces of paper more easily when
fingertips are wet with water
54