Page 145 - sarah-simblet_sketch-book-for-the-artist
P. 145
145
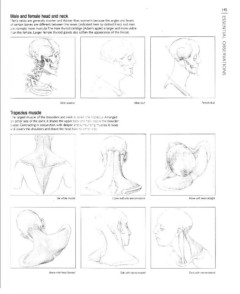
Male and female head and neck ESSENTIAL OBSERVATIONS
Men's necks are generally shorter and thicker than women's because the angles and levels
of certain bones are different between the sexes (indicated here by dotted lines) and men
are n o r m a l l y m o r e muscular. T h e male t h y r o i d cartilage ( A d a m ' s apple) is larger a n d m o r e visible
than t h e f e m a l e . L a r g e r f e m a l e t h y r o i d glands also s o f t e n t h e a p p e a r a n c e o f t h e t h r o a t .
Male skeleton Male skull Female skull
Trapezius muscle
The largest m u s c l e o f t h e s h o u l d e r s a n d n e c k is called the trapezius. A r r a n g e d
on e i t h e r side o f t h e spine, it shapes t h e u p p e r back and neck above the s h o u l d e r
blades. C o n t r a c t i n g in c o n j u n c t i o n w i t h d e e p e r and surrounding muscles, it raises
and l o w e r s t h e shoulders a n d d r a w s t h e h e a d backtoeitherside.
The whole muscle Upper half with sternomastoids Above with head straight
Above with head forward Side with sternomastoid Front with sternomastoid