Page 122 - Basic Principles of Textile Coloration
P. 122
STRUCTURE OF WOOL FIBRES 111
size and chemical nature and project outwards from the main polymer chain.
There are six main types:
(1) non-reactive hydrocarbon groups, as in alanine;
(2) polar groups such as alcoholic or phenolic groups, as in serine and tyrosine;
(3) basic groups, as in lysine, that influence the maximum amount of acid with
which the wool combines and the absorption of anionic acid dyes (Section
1.1.2)
(4) acidic groups, as in glutamic acid;
(5) covalent crosslinking groups, as in cystine, that influence the solubility,
swelling and mechanical properties of wool;
(6) heterocyclic groups, as in proline.
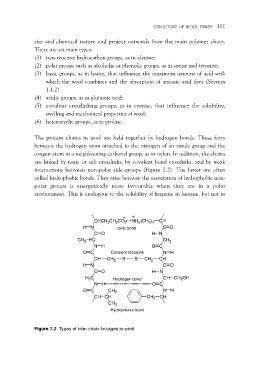
The protein chains in wool are held together by hydrogen bonds. These form
between the hydrogen atom attached to the nitrogen of an amide group and the
oxygen atom in a neighbouring carbonyl group, as in nylon. In addition, the chains
are linked by ionic or salt crosslinks, by covalent bond crosslinks, and by weak
interactions between non-polar side-groups (Figure 7.2). The latter are often
called hydrophobic bonds. They arise because the association of hydrophobic non-
polar groups is energetically more favourable when they are in a polar
environment. This is analogous to the solubility of benzene in hexane, but not in
CHCH2CH2CO2 NH3(CH2)4 CH
HN Ionic bond CO
CO HN
CH3 HC CH2
NH OC
OC Covalent crosslink NH
CH CH2 S S CH2 CH
HN CO
CO HN
H2C Hydrogen bond CH CH2OH
NH OC
OC CH3 NH
CH2 CH
CH CH
CH3
Hydrophobic bond
Figure 7.2 Types of inter-chain linkages in wool