Page 202 - Basic Principles of Textile Coloration
P. 202
Dye CONTINUOUS DYEING 191
mix tanks
Chemical
mix tanks
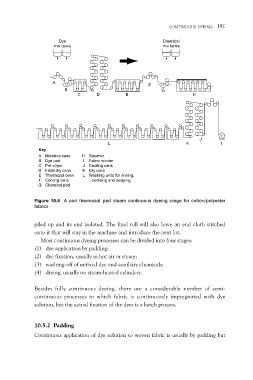
A F
B
G
C D E H
L J I
K
H Steamer
Key I Fabric winder
J Cooling cans
A Moisture cans K Dry cans
B Dye pad L Washing units for rinsing,
C Pre–dryer
D Initial dry cans oxidising and soaping
E Thermosol oven
F Cooling cans
G Chemical pad
Figure 10.6 A pad–thermosol–pad–steam continuous dyeing range for cotton/polyester
fabrics
piled up and its end isolated. The final roll will also have an end cloth stitched
onto it that will stay in the machine and introduce the next lot.
Most continuous dyeing processes can be divided into four stages:
(1) dye application by padding;
(2) dye fixation, usually in hot air or steam;
(3) washing-off of unfixed dye and auxiliary chemicals;
(4) drying, usually on steam-heated cylinders.
Besides fully continuous dyeing, there are a considerable number of semi-
continuous processes in which fabric is continuously impregnated with dye
solution, but the actual fixation of the dyes is a batch process.
10.5.2 Padding
Continuous application of dye solution to woven fabric is usually by padding but