Page 401 - Basic Principles of Textile Coloration
P. 401
390 CATIONIC DYES
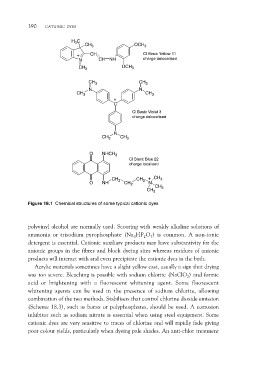
H3C CH3 OCH3
CH CI Basic Yellow 11
N CH NH charge delocalised
CH3
OCH3
CH3 CH3
N N
CH3
CH3
C
CI Basic Violet 3
charge delocalised
N
CH3 CH3
O NHCH3
CI Basic Blue 22
charge localised
O NH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
N
CH3CH3
Figure 18.1 Chemical structures of some typical cationic dyes
polyvinyl alcohol are normally used. Scouring with weakly alkaline solutions of
ammonia or trisodium pyrophosphate (Na3HP2O7) is common. A non-ionic
detergent is essential. Cationic auxiliary products may have substantivity for the
anionic groups in the fibres and block dyeing sites whereas residues of anionic
products will interact with and even precipitate the cationic dyes in the bath.
Acrylic materials sometimes have a slight yellow cast, usually a sign that drying
was too severe. Bleaching is possible with sodium chlorite (NaClO2) and formic
acid or brightening with a fluorescent whitening agent. Some fluorescent
whitening agents can be used in the presence of sodium chlorite, allowing
combination of the two methods. Stabilisers that control chlorine dioxide emission
(Scheme 18.3), such as borax or polyphosphates, should be used. A corrosion
inhibitor such as sodium nitrate is essential when using steel equipment. Some
cationic dyes are very sensitive to traces of chlorine and will rapidly fade giving
poor colour yields, particularly when dyeing pale shades. An anti-chlor treatment