Page 296 - NS-2 Textbook
P. 296
ASTRONOMY 291
()
o
FIRST QUARTER
(
GIBBOUS CRESCENT
<
(
o FULL MOON () NEW MOONe <
< SUN'S
EARTH
~ RAYS
GIBBOUS CRESCENT (
(
LAST QUARTER <
o ()
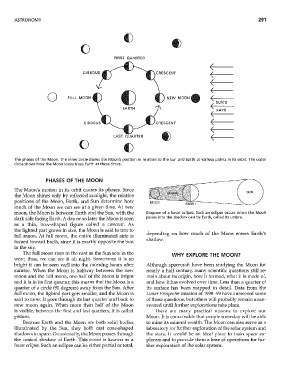
The phases of the Moon. The inner circle shows the Moon's position in relation to the Sun and Earth at various points in its orbit. The outer
circle shows how the Moon looks from Earth at these times.
PHASES OF THE MOON
The Moon's motion in its orbit causes its phases. Since
the Moon shines only by reflected sunlight, the relative
positions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun determine how
EARTH
much of the Moon vve can see at a given time. At new
moon, the Moon is between Earth and the Sun, with the Diagram of a lunar eclipse. Such an eclipse occurs when the Moon
dark side facing Earth. A day or so later the Moon is seen passes into the shadow cast by Earth, called its umbra.
as a thin, bow-shaped figure called a crescellt. As
the lighted part grows in size, the Moon is said to wax to
depending on how much of the Moon enters Earth's
full moon. At full moon, the entire illuminated side is
shadow.
turned toward Earth, since it is exactly opposite the Sun
in the sky.
The full moon rises in the east as the Sun sets in the WHY EXPLORE THE MOON?
west; thus, we can see it all night. Sometimes it is so
bright it can be seen well into the morning hours after Although spacecraft have been studying the Moon for
sunrise. When the Moon is halfway between the new nearly a half century, many scientific questions still re-
moon and the full moon, one-half of the Moon is bright main about its origin, how it formed, ,vhat it is made of,
and it is in its first quarter; this means that the Moon is a and how it has evolved over time. Less than a quarter of
quarter of a circle (90 degrees) away from the Sun. After its surface has been mapped in detail. Data from the
full moon, the lighted part gets smaller, and the Moon is LUllar Prospector mission of 1998-99 have answered some
said to walle. It goes through its last quarter and back to of these questions, but others will probably remain unan-
new moon again. When more than half of the Moon swered tmtil further explorations take place.
is visible, between the first and last quarters, it is called There are many practical reasons to explore our
gibbous. Moon. It is conceivable that people someday will be able
Because Earth and the Moon are both solid bodies to mine its nUneral "\vealth. The Moon can also serve as a
illuminated by the Sun, they both cast cone-shaped laboratory for further exploration of the solar system and
shadows in space. Occasionally, the Moon passes tlu'ough the stars. It would be an ideal place to train space ex-
the conical shadow of Earth. This event is known as a plorers and to provide them a base of operations for fur-
/ullar eclipse. Such an eclipse can be either partial or total, ther exploration of the solar system.