Page 207 - Jurnal Kurikulum BPK 2020
P. 207
RQ1: Is there a relationship between VB and depth and the MUET reading
comprehension component? In order to determine the correlation and examine the relation
between vocabulary knowledge and learners’ reading comprehension a multiple linear
regression and hierarchical regression were performed. Firstly, a two-tailed Pearson correlation
analysis was conducted and the results are displayed in Table 2. The correlations of all measures
would address RQ 1.
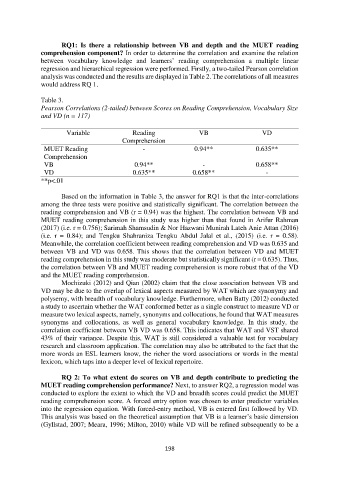
Table 3.
Pearson Correlations (2-tailed) between Scores on Reading Comprehension, Vocabulary Size
and VD (n = 117)
Variable Reading VB VD
Comprehension
MUET Reading - 0.94** 0.635**
Comprehension
VB 0.94** - 0.658**
VD 0.635** 0.658** -
**p<.01
Based on the information in Table 3, the answer for RQ1 is that the inter-correlations
among the three tests were positive and statistically significant. The correlation between the
reading comprehension and VB (r = 0.94) was the highest. The correlation between VB and
MUET reading comprehension in this study was higher than that found in Arifur Rahman
(2017) (i.e. r = 0.756); Sarimah Shamsudin & Nor Hazwani Munirah Lateh Anie Attan (2016)
(i.e. r = 0.84); and Tengku Shahraniza Tengku Abdul Jalal et al., (2015) (i.e. r = 0.58).
Meanwhile, the correlation coefficient between reading comprehension and VD was 0.635 and
between VB and VD was 0.658. This shows that the correlation between VD and MUET
reading comprehension in this study was moderate but statistically significant (r = 0.635). Thus,
the correlation between VB and MUET reading comprehension is more robust that of the VD
and the MUET reading comprehension.
Mochizuki (2012) and Qian (2002) claim that the close association between VB and
VD may be due to the overlap of lexical aspects measured by WAT which are synonymy and
polysemy, with breadth of vocabulary knowledge. Furthermore, when Batty (2012) conducted
a study to ascertain whether the WAT conformed better as a single construct to measure VD or
measure two lexical aspects, namely, synonyms and collocations, he found that WAT measures
synonyms and collocations, as well as general vocabulary knowledge. In this study, the
correlation coefficient between VB VD was 0.658. This indicates that WAT and VST shared
43% of their variance. Despite this, WAT is still considered a valuable test for vocabulary
research and classroom application. The correlation may also be attributed to the fact that the
more words an ESL learners know, the richer the word associations or words in the mental
lexicon, which taps into a deeper level of lexical repertoire.
RQ 2: To what extent do scores on VB and depth contribute to predicting the
MUET reading comprehension performance? Next, to answer RQ2, a regression model was
conducted to explore the extent to which the VD and breadth scores could predict the MUET
reading comprehension score. A forced entry option was chosen to enter predictor variables
into the regression equation. With forced-entry method, VB is entered first followed by VD.
This analysis was based on the theoretical assumption that VB is a learner’s basic dimension
(Gyllstad, 2007; Meara, 1996; Milton, 2010) while VD will be refined subsequently to be a
198