Page 210 - Jurnal Kurikulum BPK 2020
P. 210
participants who scored more than or equal to 7000 word families in VB had the tendency to
obtain more than or equal to 56 (average score) in the MUET reading comprehension
component (M=70.54, SE=0.83), than those who scored less than 7000 word families in
vocabulary knowledge (M=50.38, SE=0.78). This difference of -20.17, BCa 95%CI [-22.45, -
17.88] was significant at t (221) = -17.04, p = 0.001. In other words, since p <0.0001 is less
than our chosen significance level α = 0.05, we can reject the null hypothesis, and conclude
that the that the mean scores for reading comprehension among participants who scored more
than or equal to 7000 word families and participants who scored less than 7000 word families
is significantly different.
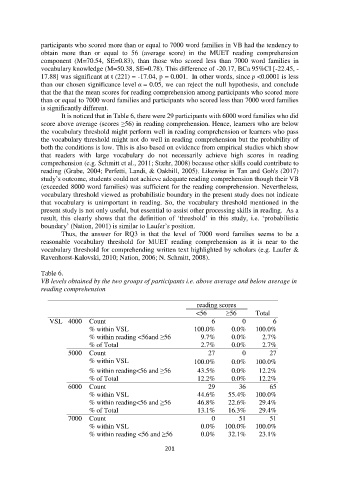
It is noticed that in Table 6, there were 29 participants with 6000 word families who did
score above average (scores ≥56) in reading comprehension. Hence, learners who are below
the vocabulary threshold might perform well in reading comprehension or learners who pass
the vocabulary threshold might not do well in reading comprehension but the probability of
both the conditions is low. This is also based on evidence from empirical studies which show
that readers with large vocabulary do not necessarily achieve high scores in reading
comprehension (e.g. Schmitt et al., 2011; Stæhr, 2008) because other skills could contribute to
reading (Grabe, 2004; Perfetti, Landi, & Oakhill, 2005). Likewise in Tan and Goh's (2017)
study’s outcome, students could not achieve adequate reading comprehension though their VB
(exceeded 8000 word families) was sufficient for the reading comprehension. Nevertheless,
vocabulary threshold viewed as probabilistic boundary in the present study does not indicate
that vocabulary is unimportant in reading. So, the vocabulary threshold mentioned in the
present study is not only useful, but essential to assist other processing skills in reading. As a
result, this clearly shows that the definition of ‘threshold’ in this study, i.e. ‘probabilistic
boundary’ (Nation, 2001) is similar to Laufer’s position.
Thus, the answer for RQ3 is that the level of 7000 word families seems to be a
reasonable vocabulary threshold for MUET reading comprehension as it is near to the
vocabulary threshold for comprehending written text highlighted by scholars (e.g. Laufer &
Ravenhorst-Kalovski, 2010; Nation, 2006; N. Schmitt, 2008).
Table 6.
VB levels obtained by the two groups of participants i.e. above average and below average in
reading comprehension
reading scores
<56 ≥56 Total
VSL 4000 Count 6 0 6
% within VSL 100.0% 0.0% 100.0%
% within reading <56and ≥56 9.7% 0.0% 2.7%
% of Total 2.7% 0.0% 2.7%
5000 Count 27 0 27
% within VSL 100.0% 0.0% 100.0%
% within reading<56 and ≥56 43.5% 0.0% 12.2%
% of Total 12.2% 0.0% 12.2%
6000 Count 29 36 65
% within VSL 44.6% 55.4% 100.0%
% within reading<56 and ≥56 46.8% 22.6% 29.4%
% of Total 13.1% 16.3% 29.4%
7000 Count 0 51 51
% within VSL 0.0% 100.0% 100.0%
% within reading <56 and ≥56 0.0% 32.1% 23.1%
201