Page 56 - Jurnal Kurikulum BPK 2018
P. 56
curriculum intention into classroom activities appropriate to his or her students (Remillard, 1999).
This second level of curriculum development is where teachers link their perception or
understanding of the curriculum to their practice, transforming curriculum plan into instruction.
How is this link being established? What kind of decision and choice teachers need to make at
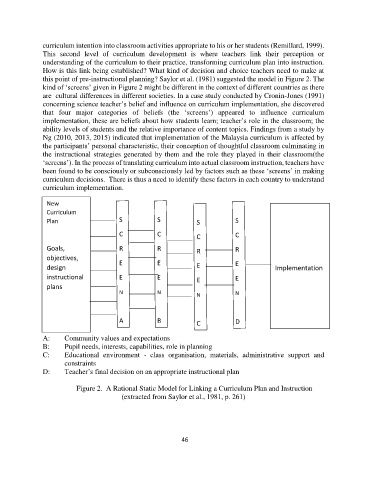
this point of pre-instructional planning? Saylor et al. (1981) suggested the model in Figure 2. The
kind of ‘screens’ given in Figure 2 might be different in the context of different countries as there
are cultural differences in different societies. In a case study conducted by Cronin-Jones (1991)
concerning science teacher’s belief and influence on curriculum implementation, she discovered
that four major categories of beliefs (the ‘screens’) appeared to influence curriculum
implementation, these are beliefs about how students learn; teacher’s role in the classroom; the
ability levels of students and the relative importance of content topics. Findings from a study by
Ng (2010, 2013, 2015) indicated that implementation of the Malaysia curriculum is affected by
the participants’ personal characteristic, their conception of thoughtful classroom culminating in
the instructional strategies generated by them and the role they played in their classroom(the
‘screens’). In the process of translating curriculum into actual classroom instruction, teachers have
been found to be consciously or subconsciously led by factors such as these ‘screens’ in making
curriculum decisions. There is thus a need to identify these factors in each country to understand
curriculum implementation.
New
Curriculum
Plan S S S S
C C C C
Goals, R R R
objectives, R
E E E E
design Implementation
instructional E E E E
plans N N
N N
A B C D
A: Community values and expectations
B: Pupil needs, interests, capabilities, role in planning
C: Educational environment - class organisation, materials, administrative support and
constraints
D: Teacher’s final decision on an appropriate instructional plan
Figure 2. A Rational Static Model for Linking a Curriculum Plan and Instruction
(extracted from Saylor et al., 1981, p. 261)
46