Page 108 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 108
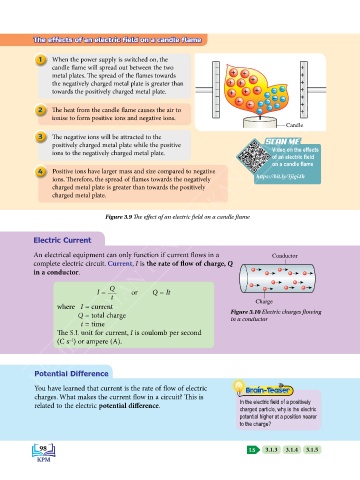
The effects of an electric field on a candle flame
1 When the power supply is switched on, the
candle flame will spread out between the two – +
metal plates. The spread of the flames towards – + + +
the negatively charged metal plate is greater than – + + + +
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
towards the positively charged metal plate. – + + + – – +
– – – – +
– + + – – – +
2 The heat from the candle flame causes the air to – – – +
ionise to form positive ions and negative ions.
Candle
3 The negative ions will be attracted to the
SCAN ME
positively charged metal plate while the positive SCAN ME
ions to the negatively charged metal plate. Video on the effects
of an electric field
on a candle flame
4 Positive ions have larger mass and size compared to negative
ions. Therefore, the spread of flames towards the negatively https://bit.ly/3jigi4h
charged metal plate is greater than towards the positively
charged metal plate.
Figure 3.9 The effect of an electric field on a candle flame
Electric Current
An electrical equipment can only function if current flows in a Conductor
complete electric circuit. Current, I is the rate of flow of charge, Q
in a conductor.
Q
I = or Q = It
t
where I = current Charge
Q = total charge Figure 3.10 Electric charges flowing
t = time in a conductor
The S.I. unit for current, I is coulomb per second
(C s ) or ampere (A).
–1
Potential Difference
You have learned that current is the rate of flow of electric Brain-Teaser
charges. What makes the current flow in a circuit? This is
related to the electric potential difference. In the electric field of a positively
charged particle, why is the electric
potential higher at a position nearer
to the charge?
98 LS 3.1.3 3.1.4 3.1.5