Page 113 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 113
Solving Problems Involving Series and Parallel Combination Circuits CHAPTER 3
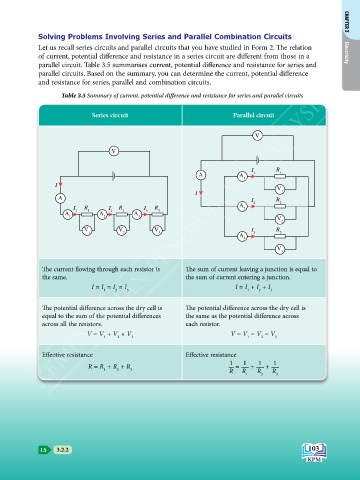
Let us recall series circuits and parallel circuits that you have studied in Form 2. The relation
of current, potential difference and resistance in a series circuit are different from those in a Electricity
parallel circuit. Table 3.5 summarises current, potential difference and resistance for series and
parallel circuits. Based on the summary, you can determine the current, potential difference
and resistance for series, parallel and combination circuits.
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
Table 3.5 Summary of current, potential difference and resistance for series and parallel circuits
Series circuit Parallel circuit
V
V
I R 1
A A 1
1
I
V
I 1
A I R
A 2 2
I R 1 I R 2 I R 3 2
A 1 A 2 A 3
1 2 3
V
2
V V V I R
1 2 3 3 3
A
3
V
3
The current flowing through each resistor is The sum of current leaving a junction is equal to
the same. the sum of current entering a junction.
I = I = I = I I = I + I + I
1 2 3 1 2 3
The potential difference across the dry cell is The potential difference across the dry cell is
equal to the sum of the potential differences the same as the potential difference across
across all the resistors. each resistor.
V = V + V + V V = V = V = V
1 2 3 1 2 3
Effective resistance Effective resistance
1 1 1 1
R = R + R + R = + +
1 2 3 R R R R
1 2 3
LS 3.2.2 103