Page 386 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 386
Chapter 8 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL RENAL NEEDS 371
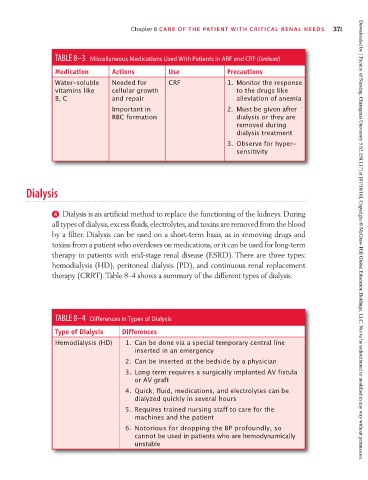
TABLE 8–3 Miscellaneous Medications Used With Patients in ARF and CRF (Continued)
Medication Actions Use Precautions
Water-soluble Needed for CRF 1. Monitor the response
vitamins like cellular growth to the drugs like
B, C and repair alleviation of anemia
Important in 2. Must be given after
RBC formation dialysis or they are
removed during
dialysis treatment
3. Observe for hyper-
sensitivity
Dialysis
4 Dialysis is an artificial method to replace the functioning of the kidneys. During
all types of dialysis, excess fluids, electrolytes, and toxins are removed from the blood
by a filter. Dialysis can be used on a short-term basis, as in removing drugs and
toxins from a patient who overdoses on medications, or it can be used for long-term Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
therapy in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). There are three types:
hemodialysis (HD), peritoneal dialysis (PD), and continuous renal replacement
therapy (CRRT). Table 8–4 shows a summary of the different types of dialysis.
TABLE 8–4 Differences in Types of Dialysis
Type of Dialysis Differences
Hemodialysis (HD) 1. Can be done via a special temporary central line
inserted in an emergency
2. Can be inserted at the bedside by a physician
3. Long term requires a surgically implanted AV fistula
or AV graft
4. Quick; fluid, medications, and electrolytes can be
dialyzed quickly in several hours
5. Requires trained nursing staff to care for the
machines and the patient
6. Notorious for dropping the BP profoundly, so
cannot be used in patients who are hemodynamically
unstable