Page 427 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 427
412 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
5. Identify the medications the patient is taking. Aspirin, anticoagulants, and other
medications can increase bleeding tendencies.
6. Check the IV site for patency for delivery of medications.
7. Administer any preprocedural medications like antianxiety and systemic
opiates, if protocol. Request medications if not.
8. Perform baseline vital signs.
9. Prepare the patient, assisting him or her into a fetal position if the posterior iliac
crest is used.
After the Procedure
1. Monitor/record VS and status of procedural site according to protocols, usually
every 15 minutes for the first hour, then every hour for the next 4 to 8 hours.
2. Assess the patient’s ability to swallow prior to allowing to eat if premedication
was given to prevent aspiration.
3. Observe for delayed hypersensitivity reactions like urticaria, itching, tachycardia,
and hypertension.
4. Report any excessive bleeding at the aspiration site.
5. Support the patient, recognizing that anxiety can result pending test results. Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Medications Commonly Used in Critical Care That Affect the
Hematologic System
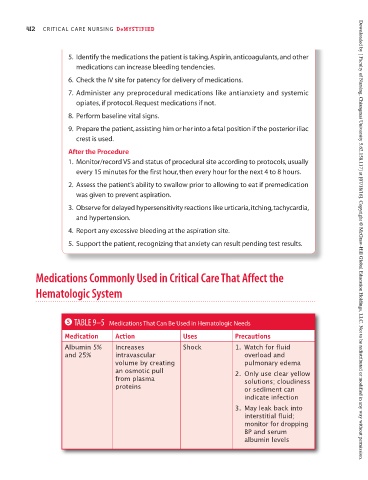
5 TABLE 9–5 Medications That Can Be Used in Hematologic Needs
Medication Action Uses Precautions
Albumin 5% Increases Shock 1. Watch for fluid
and 25% intravascular overload and
volume by creating pulmonary edema
an osmotic pull 2. Only use clear yellow
from plasma solutions; cloudiness
proteins or sediment can
indicate infection
3. May leak back into
interstitial fluid;
monitor for dropping
BP and serum
albumin levels