Page 104 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 104
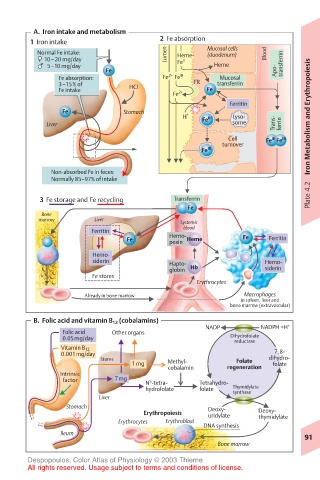
A. Iron intake and metabolism
1 Iron intake 2 Fe absorption
Normal Fe intake: Lumen Heme- Mucosal cells Blood
(duodenum)
10–20 mg/day Fe II
5–10 mg/day Heme transferrin
Fe Apo-
Fe absorption: Fe 2+ Fe III Mucosal
3–15% of HCI FR transferrin
Fe intake Fe and Erythropoiesis
Fe 2+
Ferritin
Fe Stomach
H + Fe III Lyso-
Liver some Trans- ferrin
Cell Fe Fe III
III
turnover
Fe III Iron Metabolism
Non-absorbed Fe in feces:
Normally 85–97% of intake
Plate 4.2
3 Fe storage and Fe recycling Transferrin
Fe
Bone
marrow Liver
Systemic
blood
Ferritin
Fe Hemo- Heme Fe Ferritin
pexin
Hemo-
siderin Hapto- Hemo-
globin Hb siderin
Fe stores
Erythrocytes
Already in bone marrow Macrophages
in spleen, liver and
bone marrow (extravascular)
B. Folic acid and vitamin B 12 (cobalamins)
NADP NADPH +H +
Folic acid Other organs
0.05mg/day Dihydrofolate
reductase
Vitamin B 12
0.001mg/day 7,8-
Stores Folate dihydro-
1 mg Methyl- folate
cobalamin regeneration
Intrinsic
factor 7mg N -tetra- Tetrahydro-
5
hydrofolate folate Thymidylate
synthase
Liver
Stomach Deoxy-
Erythropoiesis uridylate Deoxy-
Erythrocytes Erythroblast thymidylate
DNA synthesis
Ileum
91
Bone marrow
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.