Page 234 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 234
138 PART 2: General Management of the Patient
and marketed as an immune-enhancing diet. We use the term immu- mortality (RR 1.06; 95% CIs 0.93, 1.20; p = 0.40), no overall effect on
nonutrition as a general term to describe all these enteral products, infectious complications (RR 0.99; 95% CIs 0.85-1.15; p = 0.88), and
but attempt to make summary recommendations based on the specific a trend toward reduction in hospital length of stay (weighted mean
nutrients by themselves. difference 2.40; 95% CIs 5.90, 1.09 ; p = 0.18). The presence of sig-
86
nificant statistical heterogeneity across studies weakens the estimate
■ ARGININE of effect on length of stay.
Whether arginine-containing products worsen outcomes in critically
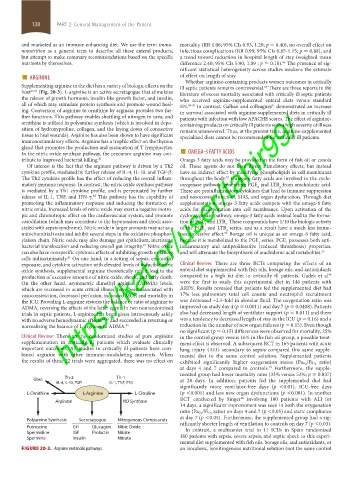
Supplementing arginine in the diet has a variety of biologic effects on the ill septic patients remains controversial. There are three reports in the
87
host 81,82 (Fig. 20-3). L-arginine is an active secretagogue that stimulates literature of excess mortality associated with critically ill septic patients
the release of growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor, and insulin, who received arginine-supplemented enteral diets versus standard
all of which may stimulate protein synthesis and promote wound heal- EN. 88-90 In contrast, Galban and colleagues demonstrated an increase
91
https://kat.cr/user/tahir99/
ing. Conversion of arginine to ornithine by arginase provides two fur- in survival associated with arginine-supplemented diets in critically ill
ther functions. This pathway enables shuttling of nitrogen to urea, and patients with infection with low APACHE scores. The effect of arginine-
ornithine is utilized in polyamine synthesis (which is involved in depo- containing products on critically ill patients with a high severity of illness
sition of hydroxyproline, collagen, and the laying down of connective remains unanswered. Thus, at the present time, arginine-supplemented
tissue to heal wounds). Arginine has also been shown to have significant specialized diets cannot be recommended for critically ill patients.
immunostimulatory effects. Arginine has a trophic effect on the thymus
In the nitric oxide synthase pathway, the precursor arginine may con- ■ OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS
gland that promotes the production and maturation of T lymphocytes.
tribute to improved bacterial killing. 81 Omega-3 fatty acids may be provided in the form of fish oil or canola
Of interest is the fact that the arginase pathway is driven by a Th2 oil. These agents do not have direct stimulatory effects, but instead
cytokine profile, mediated by further release of IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β. have an indirect effect by modifying phospholipids in cell membranes
The Th2 cytokine profile has the effect of reducing the overall inflam- throughout the body. Omega-6 fatty acids are involved in the cyclo-
92
matory immune response. In contrast, the nitric oxide synthase pathway oxygenase pathway, generating PGE and LTB from arachidonic acid.
4
2
is mediated by a Th1 cytokine profile, and is perpetuated by further These are proinflammatory cytokines that lead to immune suppression
release of IL-1, TNF, and IFN-γ. This pathway has the capability of and nosocomial infection, SIRS, and organ dysfunction. Through diet
82
promoting the inflammatory response and inducing the formation of supplementation, omega-3 fatty acids compete with the omega-6 fatty
nitric oxide. Increased levels of nitric oxide may exert a negative inotro- acids for incorporation into cell membranes. Upon activation of the
pic and chronotropic effect on the cardiovascular system, and promote cyclooxygenase pathway, omega-3 fatty acids instead lead to the forma-
vasodilation (which may contribute to the hypotension and shock asso- tion of PGE and LTB . These compounds have 1/10 the biologic activity
3
5
ciated with sepsis syndrome). Nitric oxide in larger amounts may act as a of the PGE and LTB series, and as a result have a much less immu-
2
4
mitochondrial toxin and inhibit several steps in the oxidative phosphor- nosuppressive effect. Borage oil is unique as an omega-6 fatty acid,
92
ylation chain. Nitric oxide may also damage gut epithelium, increasing because it is metabolized to the PGE series. PGE possesses both anti-
1
1
bacterial translocation and reducing overall gut integrity. Nitric oxide inflammatory and antiproliferative (reduced thrombosis) properties,
81
can also have nonspecific cytotoxic effects of inhibiting growth or killing and will attenuate the biosynthesis of arachidonic acid metabolites. 93
cells indiscriminately. On one hand, in a setting of sepsis, endotoxin
81
exposure, and cytokine activation with elevated levels of inducible nitric Clinical Review: There are three RCTs comparing the effects of an
oxide synthesis, supplemental arginine theoretically might lead to the enteral diet supplemented with fish oils, borage oils, and antioxidants
94
production of excessive amounts of nitric oxide, shock, and early death. compared to a high fat diet in critically ill patients. Gadek et al
On the other hand, asymmetric dimethyl arginine (ADMA) levels, were the first to study this experimental diet in 146 patients with
which are increased in acute critical illness, have been associated with ARDS. Results revealed that patients fed the supplemented diet had
vasoconstriction, decreased perfusion, increased MOF, and mortality in 17% less pulmonary total cell counts and neutrophil recruitment
the ICU. Providing L-arginine restores the balance or ratio of arginine to was decreased ~2.5-fold in alveolar fluid. The oxygenation ratio was
ADMA, reversing the effects of the latter agent. In two nonrandomized improved on study day 4 (p = 0.0011) and day 7 (p = 0.0408). Patients
trials in septic patients, L-arginine has been given intravenously safely also had decreased length of ventilator support (p = 0.011) and there
with no adverse hemodynamic effects, 83,84 and succeeded in reversing or was a tendency to decreased length of stay in the ICU (p = 0.16) and a
normalizing the balance of L-arginine to ADMA. 85 reduction in the number of new organ failures (p = 0.15). Even though
no significant (p = 0.15) differences were observed for mortality, 25%
Clinical Review: There are no randomized studies of pure arginine in the control group versus 16% in the fish oil group, a possible treat-
supplementation in critically ill patients which evaluate clinically ment effect is observed. A subsequent RCT in 165 patients with acute
important outcomes. All studies in critically ill patients have com- lung injury (ALI) secondary to sepsis compared this same supple-
bined arginine with other immune-modulating nutrients. When mental diet to the same control solution. Supplemented patients
the results of these 22 trials were aggregated, there was no effect on ratio)
exhibited significantly higher oxygenation status (Pa O 2 /Fi O 2
at days 4 and 7 compared to controls. Furthermore, the supple-
95
mented group had lower mortality rates (33% versus 52%; p = 0.037)
Urea Th-2 Th-1 at 28 days. In addition, patients fed the supplemented diet had
(IL-4, IL-10, TGF) (IL-1, TNF, IFN)
significantly more ventilator-free days (p <0.01), ICU-free days
L-Ornithine L-Arginine L-Citruline (p <0.001) and less new organ dysfunctions (p <0.001). In another
RCT conducted by Singer involving 100 patients with ALI for
96
Arginase NO Synthase
14 days, a significant improvement was seen in both the oxygenation
ratio) on days 4 and 7 (p <0.05) and static compliance
ratio (Pa O 2 /Fi O 2
at day 7 (p <0.05). Furthermore, the supplemented group had a sig-
Polyamine Synthesis Secretagogue Nitrogenous Compounds nificantly shorter length of ventilation to controls on day 7 (p <0.03).
Putrescine GH Glucagon Nitric Oxide In contrast, a multicenter trial in 11 ICUs in Spain randomized
Spermidine IGF Prolactin Nitrite 160 patients with sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock to this experi-
Spermine Insulin Nitrate
mental diet supplemented with fish oils, borage oils, and antioxidants, or
FIGURE 20-3. Arginine metabolic pathways. an isocaloric, isonitrogenous nutritional solution (not the same control
section02.indd 138 1/13/2015 2:04:57 PM