Page 51 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 51
20 PART 1: An Overview of the Approach to and Organization of Critical Care
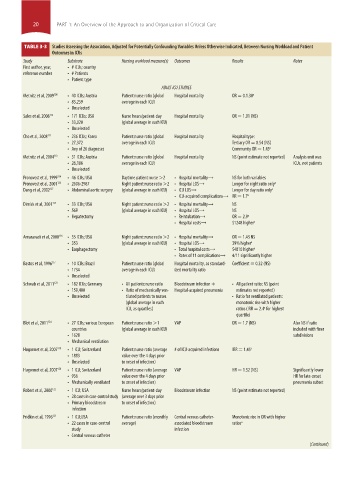
TABLE 3-3 Studies Assessing the Association, Adjusted for Potentially Confounding Variables Unless Otherwise Indicated, Between Nursing Workload and Patient
Outcomes in ICUs
Study Substrate Nursing workload measure(s) Outcomes Results Notes
First author, year, • # ICUs; country
reference number • # Patients
• Patient type
ADULT ICU STUDIES
Metnitz et al, 2009 108 • 40 ICUs; Austria Patient:nurse ratio (global Hospital mortality OR = 0.1.30 a
• 83,259 average in each ICU)
• Unselected
Sales et al, 2008 112 • 171 ICUs; USA Nurse hours/patient-day Hospital mortality OR = 1.01 (NS)
• 33,020 (global average in each ICU)
• Unselected
Cho et al, 2008 111 • 236 ICUs; Korea Patient:nurse ratio (global Hospital mortality Hospital type:
• 27,372 average in each ICU) Tertiary OR = 0.54 (NS)
• Any of 26 diagnoses Community OR = 1.43 a
Metnitz et al, 2004 113 • 31 ICUs; Austria Patient:nurse ratio (global Hospital mortality NS (point estimate not reported) Analysis unit was
• 26,186 average in each ICU) ICUs, not patients
• Unselected
Pronovost et al, 1999 114 • 46 ICUs; USA Daytime patient:nurse >2 • Hospital mortality→ NS for both variables
Pronovost et al, 2001 126 • 2606-2987 Night patient:nurse ratio >2 • Hospital LOS→ Longer for night ratio only a
Dang et al, 2002 127 • Abdominal aortic surgery (global average in each ICU) • ICU LOS→ Longer for day ratio only a
• ICU-acquired complications→ RR = 1.7 a
Dimick et al, 2001 115 • 33 ICUs; USA Night patient:nurse ratio >2 • Hospital mortality→ NS
• 569 (global average in each ICU) • Hospital LOS→ NS
• Hepatectomy • Reintubation→ OR = 2.9 a
• Hospital costs→ $1248 higher a
Amaravadi et al, 2000 116 • 35 ICUs; USA Night patient:nurse ratio >2 • Hospital mortality→ OR = 1.43 NS
• 353 (global average in each ICU) • Hospital LOS→ 39% higher a
• Esophagectomy • Total hospital costs→ $4810 higher a
• Rates of 11 complications→ 4/11 significantly higher
Bastos et al, 1996 117 • 10 ICUs; Brazil Patient:nurse ratio (global Hospital mortality, as standard- Coefficient = 0.32 (NS)
• 1734 average in each ICU) ized mortality ratio
• Unselected
Schwab et al, 2011 123 • 182 ICUs; Germany • All patients:nurse ratio Bloodstream infection + • All patient ratio: NS (point
• 159,400 • Ratio of mechanically ven- Hospital-acquired pneumonia estimates not reported)
• Unselected tilated patients to nurses • Ratio for ventilated patients:
(global average in each monotonic rise with higher
ICU, as quartiles) ratios (IRR = 2.4 for highest
a
quartile)
Blot et al, 2011 124 • 27 ICUs; various European Patient:nurse ratio >1 VAP OR = 1.7 (NS) Also NS if ratio
countries (global average in each ICU) included with finer
• 1628 subdivisions
• Mechanical ventilation
Hugonnet et al, 2007 119 • 1 ICU; Switzerland Patient:nurse ratio (average # of ICU-acquired infections IRR = 1.45 a
• 1883 value over the 4 days prior
• Unselected to onset of infection)
Hugonnet et al, 2007 120 • 1 ICU; Switzerland Patient:nurse ratio (average VAP HR = 1.52 (NS) Significantly lower
• 936 value over the 4 days prior HR for late-onset
• Mechanically ventilated to onset of infection) pneumonia subset
Robert et al, 2000 122 • 1 ICU; USA Nurse hours/patient-day Bloodstream infection NS (point estimate not reported)
• 28 cases in case-control study (average over 3 days prior
• Primary bloodstream to onset of infection)
infection
Fridkin et al, 1996 121 • 1 ICU;USA Patient:nurse ratio (monthly Central venous catheter- Monotonic rise in OR with higher
• 22 cases in case-control average) associated bloodstream ratios a
study infection
• Central venous catheter
(Continued)
Section01.indd 20 1/22/2015 9:36:46 AM