Page 52 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 52
CHAPTER 3: Intensive Care Unit Staffing 21
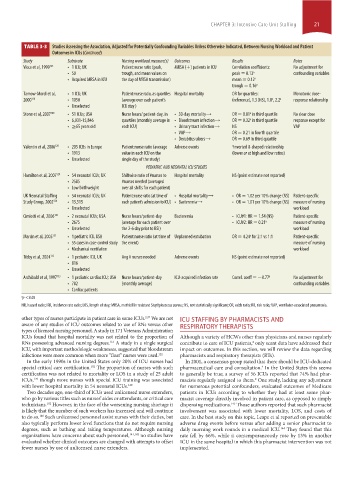
TABLE 3-3 Studies Assessing the Association, Adjusted for Potentially Confounding Variables Unless Otherwise Indicated, Between Nursing Workload and Patient
Outcomes in ICUs (Continued)
Study Substrate Nursing workload measure(s) Outcomes Results Notes
Vicca et al, 1999 125 • 1 ICU; UK Patient:nurse ratio (peak, MRSA (+) patients in ICU Correlation coefficients: No adjustment for
• 50 trough, and mean values on peak = 0.13 a confounding variables
• Acquired MRSA in ICU the day of MRSA transmission) mean = 0.12 a
trough = 0.16 a
Tarnow-Mordi et al, • 1 ICU; UK Patient:nurse ratio, as quartiles Hospital mortality OR for quartiles: Monotonic dose-
2000 110 • 1050 (average over each patient’s (reference), 1.3 (NS), 1.8 , 2.2 a response relationship
a
• Unselected ICU stay )
Stone et al, 2007 109 • 51 ICUs; USA Nurse hours/ patient-day, in • 30-day mortality→ OR = 0.81 in third quartile No clear dose
a
• 6,031-15,846 quartiles (monthly average in • Bloodstream infection→ OR = 0.32 in third quartile response except for
a
• ≥65 years old each ICU) • Urinary tract infection→ NS VAP
• VAP→ OR = 0.21 in fourth quartile
• Decubitus ulcers→ OR = 0.69 in third quartile
Valentin et al, 2006 128 • 205 ICUs in Europe Patient:nurse ratio (average Adverse events a Inverted U-shaped relationship
• 1913 value in each ICU on the (lower or at high and low ratios)
• Unselected single day of the study)
PEDIATRIC AND NEONATAL ICU STUDIES
Hamilton et al, 2007 129 • 54 neonatal ICUs; UK Shiftwise ratio of #nurses to Hospital mortality NS (point estimate not reported)
• 2585 #nurses needed (averaged
• Low birthweight over all shifts for each patient)
UK Neonatal Staffing • 54 neonatal ICUs; UK Patient:nurse ratio (at time of • Hospital mortality→ • OR = 1.02 per 10% change (NS) Patient-specific
Study Group, 2002 134 • 13,515 each patient’s admission to ICU) • Bacteremia→ • OR = 1.01 per 10% change (NS) measure of nursing
• Unselected workload
Cimiotti et al, 2006 130 • 2 neonatal ICUs; USA Nurse hours/patient-day Bacteremia • ICU#1: HR = 1.54 (NS) Patient-specific
• 2675 (average for each patient over • ICU#2: HR = 0.21 a measure of nursing
• Unselected the 2-6 day prior to BSI) workload
a
Marcin et al, 2005 131 • 1 pediatric ICU, USA Patient:nurse ratio (at time of Unplanned extubation OR = 4.24 for 2:1 vs 1:1 Patient-specific
• 55 cases in case-control study the event) measure of nursing
• Mechanical ventilation workload
Tibby et al, 2004 132 • 1 pediatric ICU, UK Avg # nurses needed Adverse events NS (point estimate not reported)
• 816
• Unselected
Archibald et al, 1997 133 • 1 pediatric cardiac ICU; USA Nurse hours/patient-day ICU-acquired infection rate Correl. coeff = −0.77 a No adjustment for
• 782 (monthly average) confounding variables
• Cardiac patients
a p <0.05
HR, hazard ratio; IRR, incidence rate ratio; LOS, length of stay; MRSA, methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus; NS, not statistically significant; OR, odds ratio; RR, risk ratio; VAP, ventilator-associated pneumonia.
other types of nurses participate in patient care in some ICUs. We are not ICU STAFFING BY PHARMACISTS AND
2,37
aware of any studies of ICU outcomes related to use of RNs versus other RESPIRATORY THERAPISTS
types of licensed nursing personnel. A study in 171 Veterans Administration
ICUs found that hospital mortality was not related to the proportion of Although a variety of HCWs other than physicians and nurses regularly
RNs possessing advanced nursing degrees. A study in a single surgical contribute to care of ICU patients, only scant data have addressed their
112
2
ICU, with important methodologic weaknesses, suggested that bloodstream impact on outcomes. In this section, we will review the data regarding
infections were more common when more “float” nurses were used. 122 pharmacists and respiratory therapists (RTs).
In the early 1990s in the United States only 20% of ICU nurses had In 2001, a consensus group stated that there should be ICU-dedicated
special critical care certification. The proportion of nurses with such pharmaceutical care and consultation. In the United States this seems
4
102
certification was not related to mortality or LOS in a study of 25 adult to generally be true; a survey of 56 ICUs reported that 74% had phar-
ICUs, though more nurses with special ICU training was associated macists regularly assigned to them. One study, lacking any adjustment
2
139
with lower hospital mortality in 54 neonatal ICUs. 129 for numerous potential confounders, evaluated outcomes of Medicare
Two decades ago, one-third of ICUs used unlicensed nurse extenders, patients in ICUs according to whether they had at least some phar-
who go by various titles such as nurses’ aides or attendants, or critical care macist coverage directly involved in patient care, as opposed to simply
technicians. However, in the face of the worsening nursing shortage it dispensing medications. Those authors reported that such pharmacist
143
102
is likely that the number of such workers has increased and will continue involvement was associated with lower mortality, LOS, and costs of
to do so. Such unlicensed personnel assist nurses with their duties, but care. In the best study on this topic, Leape et al reported on preventable
140
also typically perform lower level functions that do not require nursing adverse drug events before versus after adding a senior pharmacist to
degrees, such as bathing and taking temperatures. Although nursing daily morning work rounds in a medical ICU. They found that this
144
organizations have concerns about such personnel, 141,142 no studies have rate fell by 66%, while it contemporaneously rose by 13% in another
evaluated whether clinical outcomes are changed with attempts to offset ICU in the same hospital in which this pharmacist intervention was not
fewer nurses by use of unlicensed nurse extenders. implemented.
Section01.indd 21 1/22/2015 9:36:46 AM