Page 60 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 60
CHAPTER 4: Infection Prevention and Surveillance in the Intensive Care Unit 29
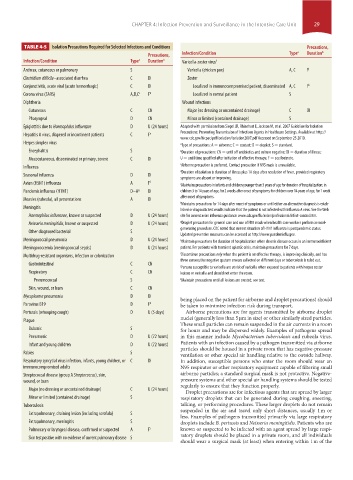
TABLE 4-5 Isolation Precautions Required for Selected Infections and Conditions Precautions,
Precautions, Infection/Condition Type a Duration b
Infection/Condition Type a Duration b Varicella-zoster virus f
Anthrax, cutaneous or pulmonary S Varicella (chicken pox) A, C F j
Clostridium difficile–associated diarrhea C DI Zoster
Conjunctivitis, acute viral (acute hemorrhagic) C DI Localized in immunocompromised patient, disseminated A, C F k
Corona virus (SARS) A,D,C c F d Localized in normal patient S
Diphtheria Wound infections
Cutaneous C CN Major (no dressing or uncontained drainage) C DI
Pharyngeal D CN Minor or limited (contained drainage) S
Epiglottitis due to Haemophilus influenzae D U (24 hours) Adapted with permission from Siegel JD, Rhinehart E, Jackson M, et al. 2007 Guideline for Isolation
Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings. Available at http://
Hepatitis A virus, diapered or incontinent patients C F e
www.cdc.gov/hicpac/pdf/isolation/Isolation2007.pdf Accessed on September 23 2010.
Herpes simplex virus a Type of precautions: A = airborne; C = contact; D = droplet; S = standard.
Encephalitis S b Duration of precautions: CN = until off antibiotics and culture negative; DI = duration of illness;
Mucocutaneous, disseminated or primary, severe C DI U = until time specified after initiation of effective therapy; F = see footnote.
c Airborne precaution is preferred. Contact precaution if N95 mask is unavailable.
Influenza
d Duration of isolation is duration of illness plus 10 days after resolution of fever, provided respiratory
Seasonal influenza D DI
symptoms are absent or improving.
Avian (H5N1) influenza A F f e Maintains precautions in infants and children younger than 3 years of age for duration of hospitalization; in
Pandemic influenza (H1N1) D~A g DI children 3 to 14 years of age, for 2 weeks after onset of symptoms; for children over 14 years of age, for 1 week
after onset of symptoms.
Measles (rubeola), all presentations A DI
f Maintains precautions for 14 days after onset of symptoms or until either an alternative diagnosis is estab-
Meningitis
lished or diagnostic test results indicate that the patient is not infected with influenza A virus. See the Web
Haemophilus influenzae, known or suspected D U (24 hours) site for current avian influenza guidance: www.cdc.gov/flu/avian/professional/infect-control.htm.
Neisseria meningitidis, known or suspected D U (24 hours) g Droplet precaution for general care and use of N95 mask when health care workers perform aerosol-
generating procedure. CDC noted that current situation of H1N1 influenza is postpandemic status.
Other diagnosed bacterial S
Updated preventive measures can be accessed at http://www.pandemicflu.gov.
Meningococcal pneumonia D U (24 hours) h Maintain precautions for duration of hospitalization when chronic disease occurs in an immunodeficient
Meningococcemia (meningococcal sepsis) D U (24 hours) patient. For patients with transient aplastic crisis, maintain precautions for 7 days.
Multidrug-resistant organisms, infection or colonization i Discontinue precautions only when the patient is on effective therapy, is improving clinically, and has
three consecutive negative sputum smears collected on different days or tuberculosis is ruled out.
Gastrointestinal C CN
j Persons susceptible to varicella are at risk of varicella when exposed to patients with herpes zoster
Respiratory C CN lesions or varicella and should not enter the room.
Pneumococcal S k Maintain precautions until all lesions are crusted; see text.
Skin, wound, or burn C CN
Mycoplasma pneumonia D DI
being placed on the patient for airborne and droplet precautions) should
Parovirus B19 D F h be taken to minimize infection risk during transport.
Pertussis (whooping cough) D U (5 days) Airborne precautions are for agents transmitted by airborne droplet
nuclei (generally less than 5 μm in size) or other similarly sized particles.
Plague
These small particles can remain suspended in the air currents in a room
Bubonic S for hours and may be dispersed widely. Examples of pathogens spread
Pneumonic D U (72 hours) in this manner include Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rubeola virus.
Infant and young children D U (72 hours) Patients with an infection caused by a pathogen transmitted via airborne
particles should be housed in a private room that has negative-pressure
Rabies S ventilation or other special air handling relative to the outside hallway.
Respiratory syncytial virus infection, infants, young children, or C DI In addition, susceptible persons who enter the room should wear an
immunocompromised adults N95 respirator or other respiratory equipment capable of filtering small
Streptococcal disease (group A Streptococcus), skin, airborne particles; a standard surgical mask is not protective. Negative-
wound, or burn pressure systems and other special air handling systems should be tested
regularly to ensure that they function properly.
Major (no dressing or uncontained drainage) C U (24 hours)
Droplet precautions are for infectious agents that are spread by larger
Minor or limited (contained drainage) S respiratory droplets that can be generated during coughing, sneezing,
Tuberculosis talking, or performing procedures. These larger droplets do not remain
suspended in the air and travel only short distances, usually 1 m or
Extrapulmonary, draining lesion (including scrofula) S
less. Examples of pathogens transmitted primarily via large respiratory
Extrapulmonary, meningitis S droplets include B. pertussis and Neisseria meningitidis. Patients who are
Pulmonary or laryngeal disease, confirmed or suspected A F i known or suspected to be infected with an agent spread by large respi-
ratory droplets should be placed in a private room, and all individuals
Skin test positive with no evidence of current pulmonary disease S
should wear a surgical mask (at least) when entering within 1 m of the
Section01.indd 29 1/22/2015 9:36:48 AM