Page 865 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 865
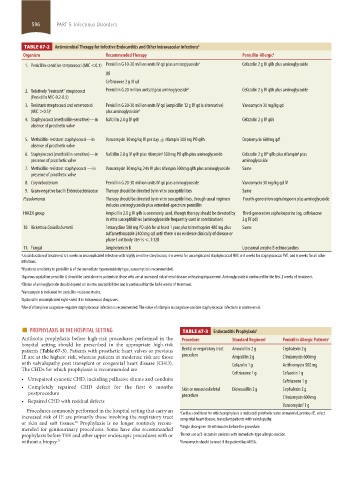
596 PART 5: Infectious Disorders
TABLE 67-2 Antimicrobial Therapy for Infective Endocarditis and Other Intravascular Infections a
Organism Recommended Therapy Penicillin-Allergic b
1. Penicillin-sensitive streptococci (MIC <0.1) Penicillin G 10-20 million units IV qd plus aminoglycoside c Cefazolin 2 g IV q8h plus aminoglycoside
OR
Ceftriaxone 2 g IV qd
2. Relatively “resistant” streptococci Penicillin G 20 million units/d plus aminoglycoside d Cefazolin 2 g IV q8h plus aminoglycoside
(Penicillin MIC-0.2-0.5)
3. Resistant streptococci and enterococci Penicillin G 20-30 million units IV qd (ampicillin 12 g IV qd is alternative) Vancomycin 30 mg/kg qd
(MIC >0.5) e plus aminoglycoside d
4. Staphylococci (methicillin-sensitive)—in Nafcillin 2.0 g IV q4h Cefazolin 2 g IV q8h
absence of prosthetic valve
5. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci—in Vancomycin 30 mg/kg IV per day ± rifampin 300 mg PO q8h Daptomycin 600mg qd f
absence of prosthetic valve
g
g
b
6. Staphylococci (methicillin-sensitive)—in Nafcillin 2.0 g IV q4h plus rifampin 300 mg PO q8h plus aminoglycoside Cefazolin 2 g IV q8h plus rifampin plus
presence of prosthetic valve aminoglycoside
7. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci —in Vancomycin 30 mg/kg 24h IV plus rifampin 300 mg q8h plus aminoglycoside Same
presence of prosthetic valve
8. Corynebacterium Penicillin G 20-30 million units IV qd plus aminoglycoside Vancomycin 30 mg/kg qd IV
9. Gram-negative bacilli Enterobacteriaceae Therapy should be directed by in vitro susceptibilities Same
Pseudomonas Therapy should be directed by in vitro susceptibilities, though usual regimen Fourth-generation cephalosporin plus aminoglycoside
includes aminoglycoside plus extended-spectrum penicillin
HACEK group Ampicillin 2.0 g IV q4h is commonly used, though therapy should be directed by Third-generation cephalosporins (eg, ceftriaxone
in vitro susceptibilities (aminoglycoside frequently used in combination) 2 g IV qd)
10. Rickettsia Coxiella burnetii Tetracycline 500 mg PO q6h for at least 1 year plus trimethoprim 480 mg plus Same
sulfamethoxazole 2400 mg qd until there is no evidence clinically of disease or
phase I antibody titer is <.1:128
11. Fungal Amphotericin B Liposomal ampho B echinocandins
a Usual duration of treatment is 4 weeks in uncomplicated infection with highly sensitive streptococci, 4-6 weeks for uncomplicated staphylococcal NVE, 6-8 weeks for staphylococcal PVE, and 6 weeks for all other
infections.
b If patient sensitivity to penicillin is of the immediate hypersensitivity type, vancomycin is recommended.
c Aqueous crystalline penicillin G should be used alone in patients in those who are at increased risk of renal disease or hearing impairment. Aminoglycoside is continued for the first 2 weeks of treatment.
d Choice of aminoglycoside should depend on in vitro susceptibilities and is continued for the full 6 weeks of treatment.
e Vancomycin is indicated for penicillin-resistant strains.
f Optional in uncomplicated right-sided IE in intravenous drug users.
g Use of rifampin in coagulase-negative staphylococcal infection is recommended. The value of rifampin in coagulase-positive staphylococcal infections is controversial.
■ PROPHYLAXIS IN THE HOSPITAL SETTING TABLE 67-3 Endocarditis Prophylaxis a
Antibiotic prophylaxis before high-risk procedures performed in the Procedure Standard Regimen b Penicillin Allergic Patients c
hospital setting should be prescribed in the appropriate high-risk
patients (Table 67-3). Patients with prosthetic heart valves or previous Dental or respiratory tract Amoxicillin 2 g Cephalexin 2 g
IE are at the highest risk, whereas patients at moderate risk are those procedure Ampicillin 2 g Clindamycin 600 mg
with valvulopathy post transplant or congenital heart disease (CHD). Cefazolin 1 g Azithromycin 500 mg
The CHDs for which prophylaxis is recommended are
Ceftriaxone 1 g Cefazolin 1 g
• Unrepaired cyanotic CHD, including palliative shunts and conduits Ceftriaxone 1 g
• Completely repaired CHD defect for the first 6 months Skin or musculoskeletal Dicloxacillin 2 g Cephalexin 2 g
postprocedure procedure
• Repaired CHD with residual defects Clindamycin 600 mg
Vancomycin 1 g
d
Procedures commonly performed in the hospital setting that carry an a
Cardiac conditions for which prophylaxis is indicated: prosthetic valve or material, previous IE, select
increased risk of IE are primarily those involving the respiratory tract congenital heart disease, transplant patients with valvulopathy.
or skin and soft tissues. Prophylaxis is no longer routinely recom-
30
mended for genitourinary procedures. Some have also recommended b Single dose given 30-60 minutes before the procedure.
prophylaxis before TEE and other upper endoscopic procedures with or c Do not use a β-lactam in patients with immediate-type allergic reaction.
without a biopsy. 31 d Vancomycin should be used if the patient has MRSA.
section05_c61-73.indd 596 1/23/2015 12:48:01 PM