Page 903 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 903
634 PART 5: Infectious Disorders
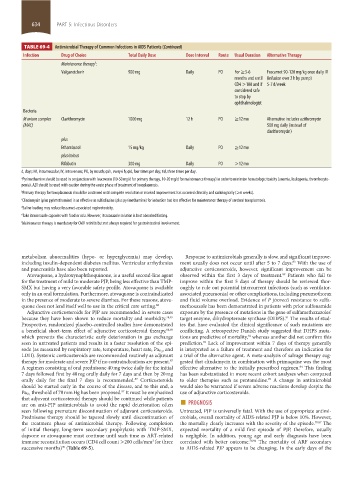
TABLE 69-4 Antimicrobial Therapy of Common Infections in AIDS Patients (Continued)
Infection Drug of Choice Total Daily Dose Dose Interval Route Usual Duration Alternative Therapy
Maintenance therapy: f
Valganciclovir 900 mg Daily PO For ≥3-6 Foscarnet 90-120 mg/kg once daily IV
months and until (infusion over 2 h by pump)
CD4 >100 and if 5-7 d/week
considered safe
to stop by
ophthalmologist
Bacteria
M avium complex Clarithromycin 1000 mg 12 h PO ≥12 mo Alternative includes azithromycin
(MAC) 500 mg daily (instead of
clarithromycin)
plus
Ethambutol 15 mg/kg Daily PO ≥12 mo
plus/minus
Rifabutin 300 mg Daily PO >12 mo
d, days; IM, intramuscular; IV, intravenous; PO, by mouth; q6h, every 6 h; qid, four times per day; tid, three times per day.
a Pyrimethamine should be used in conjunction with leucovorin (10-50 mg/d for primary therapy, 10-20 mg/d for maintenance therapy) in order to minimize hematologic toxicity (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocyto-
penia). AZT should be used with caution during the acute phase of treatment of toxoplasmosis.
b Primary therapy for toxoplasmosis should be continued until complete resolution or marked improvement has occurred clinically and radiologically (≥6 weeks).
c Clindamycin (plus pyrimethamine) is as effective as sulfadiazine (plus pyrimethamine) for induction but less effective for maintenance therapy of cerebral toxoplasmosis.
d Saline loading may reduce foscarnet-associated nephrotoxicity.
e Take itraconazole capsules with food or cola. However, itraconazole solution is best absorbed fasting.
f Maintenance therapy is mandatory for CMV retinitis but not always required for gastrointestinal involvement.
metabolism abnormalities (hypo- or hyperglycemia) may develop, Response to antimicrobials generally is slow, and significant improve-
including insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ventricular arrhythmias ment usually does not occur until after 5 to 7 days. With the use of
83
and pancreatitis have also been reported. adjunctive corticosteroids, however, significant improvement can be
Atovaquone, a hydroxynaphthoquinone, is a useful second-line agent observed within the first 3 days of treatment. Patients who fail to
89
for the treatment of mild to moderate PJP, being less effective than TMP- improve within the first 5 days of therapy should be reviewed thor-
SMX but having a very favorable safety profile. Atovaquone is available oughly to rule out potential intercurrent infections (such as ventilator-
only in an oral formulation. Furthermore, atovaquone is contraindicated associated pneumonia) or other complications, including pneumothorax
in the presence of moderate to severe diarrhea. For these reasons, atova- and fluid volume overload. Evidence of P jirovecii resistance to sulfa-
quone does not lend itself well to use in the critical care setting. 86 methoxazole has been demonstrated in patients with prior sulfonamide
Adjunctive corticosteroids for PJP are recommended in severe cases exposure by the presence of mutations in the gene of sulfamethaxazoles’
because they have been shown to reduce mortality and morbidity. 78,87 target enzyme, dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). The results of stud-
91
Prospective, randomized placebo-controlled studies have demonstrated ies that have evaluated the clinical significance of such mutations are
a beneficial short-term effect of adjunctive corticosteroid therapy, 88,89 conflicting. A retrospective Danish study suggested that DHPS muta-
92
which prevents the characteristic early deterioration in gas exchange tions are predictive of mortality, whereas another did not confirm this
seen in untreated patients and results in a faster resolution of the epi- prediction. Lack of improvement within 7 days of therapy generally
93
, and is interpreted as a failure of treatment and therefore an indication for
sode (as measured by respiratory rate, temperature, heart rate, Pa O 2
LDH). Systemic corticosteroids are recommended routinely as adjuvant a trial of the alternative agent. A meta-analysis of salvage therapy sug-
therapy for moderate and severe PJP if no contraindications are present. gested that clindamycin in combination with primaquine was the most
87
A regimen consisting of oral prednisone 40 mg twice daily for the initial effective alternative to the initially prescribed regimen. This finding
94
7 days followed first by 40 mg orally daily for 7 days and then by 20 mg has been substantiated in more recent cohort analyses when compared
orally daily for the final 7 days is recommended. Corticosteroids to older therapies such as pentamidine. A change in antimicrobial
87
95
should be started early in the course of the disease, and to this end, a would also be warranted if severe adverse reactions develop despite the
threshold of 70 mm Hg has been proposed. It must be emphasized
use of adjunctive corticosteroids.
87
are on anti-PJP antimicrobials to avoid the rapid deterioration often ■ PROGNOSIS
Pa O 2
that adjuvant corticosteroid therapy should be continued while patients
seen following premature discontinuation of adjuvant corticosteroids. Untreated, PJP is universally fatal. With the use of appropriate antimi-
Prednisone therapy should be tapered slowly until discontinuation of crobials, overall mortality of AIDS-related PJP is below 10%. However,
the treatment phase of antimicrobial therapy. Following completion the mortality clearly increases with the severity of the episode. 78,87 The
of initial therapy, long-term secondary prophylaxis with TMP-SMX, expected mortality of a mild first episode of PJP, therefore, usually
dapsone or atovaquone must continue until such time as ART-related is negligible. In addition, young age and early diagnosis have been
immune reconstitution occurs (CD4 cell count >200 cells/mm for three correlated with better outcome. 78,96 The mortality of ARF secondary
3
90
successive months) (Table 69-5). to AIDS-related PJP appears to be changing. In the early days of the
section05_c61-73.indd 634 1/23/2015 12:48:21 PM