Page 908 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 908
CHAPTER 69: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and AIDS in the Intensive Care Unit 639
New or worsening headache or CNS
dysfunction in late HIV infection
MRI or CT (contrast) showing
mass lesion or shift
No
Yes
Lumbar puncture
Positive serum If strongly suggestive
toxoplasma serology of PCNSL a Spinal fluid: positive culture,
antigen, PCR, or VDRL
Yes No
Yes No
Treat for Consider
Empiric therapy for Lumbar puncture Cryptococcal, TB, or metabolic or toxic
toxoplasmosis considered safe other meningitis, or encephalopathy,
CMV or HSV AIDS dementia
encephalitis, or complex, vascular
Neurosyphilis, or lesions, and others
PML (JC virus)
No Yes
Improved clinically Positive CSF
and by neuroimaging cytology or EBV
after 7-14 days PCR
Yes No No Yes
Continue therapy Consider stereotactic Treat for PCNSL (consider
for toxoplasmosis brain biopsy brain biopsy confirmation)
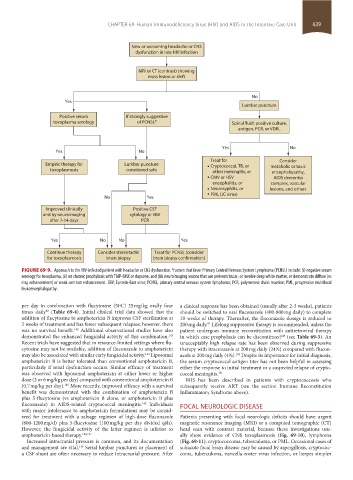
FIGURE 69-9. Approach to the HIV-infected patient with headache or CNS dysfunction. Factors that favor Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) include: (i) negative serum
a
serology for toxoplasma, (ii) on chronic prophylaxis with TMP-SMX or dapsone, and (iii) neuroimaging lesions that are periventricular, or involve deep white matter, or demonstrate diffuse (vs
ring enhancement) or weak contrast enhancement. EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; PCNSL, primary central nervous system lymphoma; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PML, progressive multifocal
leukoencephalopathy.
per day in combination with flucytosine (5FC) 25 mg/kg orally four a clinical response has been obtained (usually after 2-3 weeks), patients
times daily (Table 69-4). Initial clinical trial data showed that the should be switched to oral fluconazole (400-800 mg daily) to complete
82
addition of flucytosine to amphotericin B improves CSF sterilization at 10 weeks of therapy. Thereafter, the fluconazole dosage is reduced to
2 weeks of treatment and has fewer subsequent relapses; however, there 200 mg daily. Lifelong suppressive therapy is recommended, unless the
82
was no survival benefit. Additional observational studies have also patient undergoes immune reconstitution with antiretroviral therapy
142
demonstrated the enhanced fungicidal activity of this combination. in which case prophylaxis can be discontinued (see Table 69-5). An
143
149
Recent trials have suggested that in resource-limited settings where flu- unacceptably high relapse rate has been observed during suppressive
cytosine may not be available, addition of fluconazole to amphotericin therapy with itraconazole at 200 mg daily (24%) compared with flucon-
may also be associated with similar early fungicidal activity. Liposomal azole at 200 mg daily (4%). Despite its importance for initial diagnosis,
150
144
amphotericin B is better tolerated than conventional amphotericin B, the serum cryptococcal antigen titer has not been helpful in assessing
particularly if renal dysfunction occurs. Similar efficacy of treatment either the response to initial treatment or a suspected relapse of crypto-
was observed with liposomal amphotericin at either lower or higher coccal meningitis. 151
dose (3 or 6 mg/kg per day) compared with conventional amphotericin B IRIS has been described in patients with cryptococcosis who
(0.7 mg/kg per day). More recently, improved efficacy with a survival subsequently receive ART (see the section Immune Reconstitution
145
benefit was demonstrated with the combination of amphotericin B Inflammatory Syndrome above).
plus 5-flucytosine (vs amphotericin B alone, or amphotericin B plus
fluconazole) in AIDS-related cryptococcal meningitis. Individuals FOCAL NEUROLOGIC DISEASE
142
with major intolerance to amphotericin formulations may be consid-
ered for treatment with a salvage regimen of high-dose fluconazole Patients presenting with focal neurologic deficits should have urgent
(800-1200 mg/d) plus 5-flucytosine (100 mg/kg per day divided q6h). magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a computed tomographic (CT)
However, the fungicidal activity of the latter regimen is inferior to head scan with contrast material, because these investigations usu-
amphotericin-based therapy. 146,147 ally show evidence of CNS toxoplasmosis (Fig. 69-10), lymphoma
Increased intracranial pressure is common, and its documentation (Fig. 69-11), cryptococcoma, tuberculoma, or PML. Occasional cases of
and management are vital. Serial lumbar punctures or placement of subacute focal brain disease may be caused by aspergillosis, cryptococ-
148
a CSF shunt are often necessary to reduce intracranial pressure. After coma, tuberculoma, varicella-zoster virus infection, or herpes simplex
section05_c61-73.indd 639 1/23/2015 12:48:23 PM