Page 909 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 909
640 PART 5: Infectious Disorders
encephalitis. PML usually presents with radiologic evidence of white
matter disease without mass effect. The abrupt onset of focal neuro-
logic deficit suggests either a seizure or vascular disorder. Patients with
a CT scan or MRI compatible with toxoplasmosis should be treated
empirically with pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine in combination with
leucovorin, or alternatively pyrimethamine and clindamycin again in
combination with leucovorin (to alleviate the hematologic toxicities of
pyrimethamine). The diagnosis of toxoplasmosis usually is presump-
82
tive based on (1) positive toxoplasmosis serology (IgG antibody) in most
individuals, (2) compatible neuroimaging, and (3) subsequent clinical
and radiologic response to empiric therapy. Corticosteroids should
152
be given (dexamethasone 4 mg q6h) if there is brain imaging showing a
midline shift, or signs of critically elevated intracranial pressure, or early
clinical deterioration within the first 48 hours of treatment. However,
lymphoma may respond transiently to corticosteroids, confounding
the assessment of response to toxoplasmosis therapy and also reducing
the diagnostic yield of any subsequent brain biopsy. Early brain biopsy
should be considered for patients with mass lesion(s) who are less likely
to have toxoxplasmosis based on the combination of neuroimaging find-
ings, negative toxoplasma serology, and whether the patient developed
the lesions while taking TMP-SMX prophylaxis. Those who do not
respond to a short (10 day) course of empiric toxoplasma therapy should
be considered for brain biopsy. Initiation of ART has been associated
with improved clinical course and survival time in HIV-related PML for
the subset of patients having relatively high CD4 counts and low spinal
fluid JC viral load at the time of diagnosis. JC viral load in spinal fluid
153
usually becomes undetectable for PML patients who respond to ART.
No antiviral agent directed against JC virus has been demonstrated to
be effective in the management of PML. Neurosyphilis is responsible
154
only occasionally for focal neurologic deficit, but it is important to con-
sider this treatable condition.
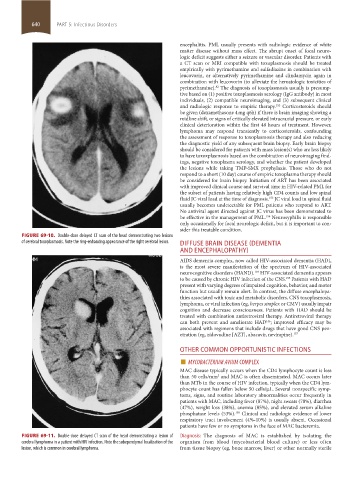
FIGURE 69-10. Double-dose delayed CT scan of the head demonstrating two lesions
of cerebral toxoplasmosis. Note the ring-enhancing appearance of the right cerebral lesion. DIFFUSE BRAIN DISEASE (DEMENTIA
AND ENCEPHALOPATHY)
AIDS dementia complex, now called HIV-associated dementia (HAD),
is the most severe manifestation of the spectrum of HIV-associated
neurocognitive disorders (HAND). HIV-associated dementia appears
139
to be caused by chronic HIV infection of the CNS. Patients with HAD
155
present with varying degrees of impaired cognition, behavior, and motor
function but usually remain alert. In contrast, the diffuse encephalopa-
thies associated with toxic and metabolic disorders, CNS toxoplasmosis,
lymphoma, or viral infection (eg, herpes simplex or CMV) usually impair
cognition and decrease consciousness. Patients with HAD should be
treated with combination antiretroviral therapy. Antiretroviral therapy
can both prevent and ameliorate HAD ; improved efficacy may be
156
associated with regimens that include drugs that have good CNS pen-
etration (eg, zidovudine [AZT], abacavir, nevirapine). 157
OTHER COMMON OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS
■ MYCOBACTERIUM AVIUM COMPLEX
MAC disease typically occurs when the CD4 lymphocyte count is less
than 50 cells/mm and MAC is often disseminated. MAC occurs later
3
than MTb in the course of HIV infection, typically when the CD4 lym-
phocyte count has fallen below 50 cells/µL. Several nonspecific symp-
toms, signs, and routine laboratory abnormalities occur frequently in
patients with MAC, including fever (87%), night sweats (78%), diarrhea
(47%), weight loss (38%), anemia (85%), and elevated serum alkaline
phosphatase levels (53%). Clinical and radiologic evidence of lower
158
respiratory tract involvement (4%-10%) is usually absent. Occasional
patients have few or no symptoms in the face of MAC bacteremia.
FIGURE 69-11. Double-dose delayed CT scan of the head demonstrating a lesion of Diagnosis: The diagnosis of MAC is established by isolating the
cerebral lymphoma in a patient with HIV infection. Note the subependymal localization of the organism from blood (mycobacterial blood culture) or less often
lesion, which is common in cerebral lymphoma. from tissue biopsy (eg, bone marrow, liver) or other normally sterile
section05_c61-73.indd 640 1/23/2015 12:48:24 PM