Page 92 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 92
60 PART 1: An Overview of the Approach to and Organization of Critical Care
the community’s plan for mass casualty and medical surge augments trained in and assigned roles within HICS. A general understanding of
the process of scarce resource management. This optimizes health care how processes differ when HICS is utilized for incident management
delivery to both the local ICU and the critically ill patients within a com- and how the ICU integrates into those efforts with proper communica-
munity or region during a catastrophe. tion ensures adequate health care delivery in the management of poten-
■ ORGANIZING THE HOSPITAL FOR DISASTER RESPONSE tially scarce resources. The use of HICS within hospitals also provides
the common and accepted organization and language for incident man-
The US National Incident Management System (NIMS) is the frame- agement to streamline interaction with supporting community agencies.
40
work by which local, state, and federal agencies organize to prepare for
and respond to emergencies. NIMS provides a standard structure and
terminology so that responders across multiple agencies utilize the same
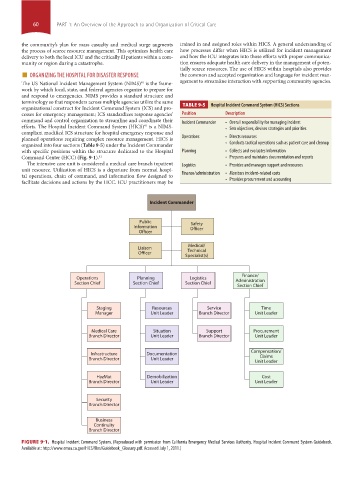
organizational construct for Incident Command System (ICS) and pro- TABLE 9-5 Hospital Incident Command System (HICS) Sections
cesses for emergency management; ICS standardizes response agencies’ Position Description
command and control organization to streamline and coordinate their Incident Commander • Overall responsibility for managing incident
efforts. The Hospital Incident Command System (HICS) is a NIMS- • Sets objectives, devises strategies and priorities
41
compliant modified ICS structure for hospital emergency response and
planned operations requiring complex resource management. HICS is Operations • Directs resources
organized into four sections (Table 9-5) under the Incident Commander • Conducts tactical operations such as patient care and cleanup
with specific positions within the structure dedicated to the Hospital Planning • Collects and evaluates information
Command Center (HCC) (Fig. 9-1). 41 • Prepares and maintains documentation and reports
The intensive care unit is considered a medical care branch inpatient Logistics • Provides and manages support and resources
unit resource. Utilization of HICS is a departure from normal hospi-
tal operations, chain of command, and information flow designed to Finance/administration • Monitors incident-related costs
facilitate decisions and actions by the HCC. ICU practitioners may be • Provides procurement and accounting
Incident Commander
Public Safety
Information Officer
Officer
Medical/
Liaison Technical
Officer
Specialist(s)
Finance/
Operations Planning Logistics Administration
Section Chief Section Chief Section Chief
Section Chief
Staging Resources Service Time
Manager Unit Leader Branch Director Unit Leader
Medical Care Situation Support Procurement
Branch Director Unit Leader Branch Director Unit Leader
Compensation/
Infrastructure Documentation Claims
Branch Director Unit Leader
Unit Leader
HazMat Demobilization Cost
Branch Director Unit Leader Unit Leader
Security
Branch Director
Business
Continuity
Branch Director
FIGURE 9-1. Hospital Incident Command System. (Reproduced with permission from California Emergency Medical Services Authority. Hospital Incident Command System Guidebook.
Available at: http://www.emsa.ca.gov/HICS/files/Guidebook_Glossary.pdf. Accessed July 1, 2011.)
Section01.indd 60 1/22/2015 9:37:06 AM