Page 93 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 93
CHAPTER 9: Preparedness for Catastrophe 61
Notes:
- All MEMS components
Medical Control have established
Center (MCC) communication and
coordination links.
Community In Home Care - The MCC oversees all
operations.
Outreach (CO) - The CTS transports
casualties between all
MEMS components.
- If the NEHC operates
as a POD or VC, then
the population at risk is
processed through and
Neighborhood Worried Well returns to work/home.
Casualties & Acute Care - Special Needs Shelters
Worried Well Emergency Help Centers (ACC) Area Hospitals Return to will receive patients
Centers (NEHC) Work/Home
from ACC based on their
medical needs.
- Mass Care Shelters will
house nonmedical
Casualty evacuees.
Assumptions:
Transportation - Although the primary
System (CTS) point of entry into MEMS
Casualties is the NEHC, patients
Hospitals and Treated or will self-present to
hospitals, ACC, and any
Clinics Out-of- Fatality Convalescing other available medical
Area for Non- Management at Home resource.
Incident Patients
Resources & Patient Flow
Information Flow
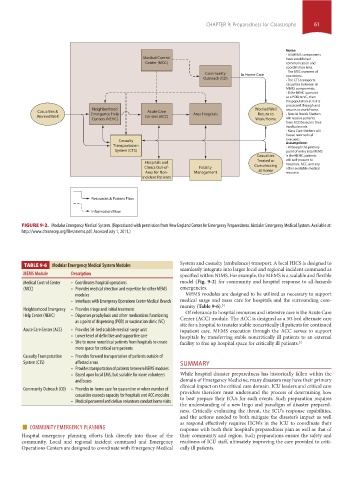
FIGURE 9-2. Modular Emergency Medical System. (Reproduced with permission from New England Center for Emergency Preparedness. Modular Emergency Medical System. Available at:
http://www.dmsnecep.org/files/mems.pdf. Accessed July 1, 2011.)
System and casualty (ambulance) transport. A local HICS is designed to
TABLE 9-6 Modular Emergency Medical System Modules
seamlessly integrate into larger local and regional incident command as
MEMS Module Description specified within NIMS. For example, the MEMS is a scalable and flexible
Medical Control Center • Coordinates hospital operations model (Fig. 9-2) for community and hospital response to all-hazards
(MCC) • Provides medical direction and expertise for other MEMS emergencies.
modules MEMS modules are designed to be utilized as necessary to support
• Interfaces with Emergency Operations Center Medical Branch medical surge and mass care for hospitals and the surrounding com-
munity (Table 9-6). 24
Neighborhood Emergency • Provides triage and initial treatment Of relevance to hospital resources and intensive care is the Acute Care
Help Center (NEHC) • Dispenses prophylaxis and other medications functioning Center (ACC) module. The ACC is designed as a 50-bed alternate care
as a point of dispensing (POD) or vaccination clinic (VC)
site for a hospital to transfer stable noncritically ill patients for continued
Acute Care Center (ACC) • Provides 50-bed scalable medical surge unit inpatient care. MEMS execution through the ACC serves to support
• Lower level of definitive and supportive care hospitals by transferring stable noncritically ill patients to an external
• Site to move noncritical patients from hospitals to create facility to free up hospital space for critically ill patients. 24
more space for critical care patients
Casualty Transportation • Provides forward transportation of patients outside of
System (CTS) affected areas SUMMARY
• Provides transportation of patients between MEMS modules
• Based upon local EMS, but scalable for more volunteers While hospital disaster preparedness has historically fallen within the
and buses domain of Emergency Medicine, many disasters may have their primary
clinical impact on the critical care domain. ICU leaders and critical care
Community Outreach (CO) • Provides in-home care for quarantine or when number of providers therefore must understand the process of determining how
casualties exceeds capacity for hospitals and ACC modules to best prepare their ICUs for such events. Such preparation requires
• Medical personnel and civilian volunteers conduct home visits
the understanding of a new lingo and paradigm of disaster prepared-
ness. Critically evaluating the threat, the ICU’s response capabilities,
and the actions needed to both mitigate the disaster’s impact as well
■ COMMUNITY EMERGENCY PLANNING as respond effectively requires HCWs in the ICU to coordinate their
response with both their hospital’s preparedness plan as well as that of
Hospital emergency planning efforts link directly into those of the their community and region. Such preparations ensure the safety and
community. Local and regional incident command and Emergency readiness of ICU staff, ultimately improving the care provided to criti-
Operations Centers are designed to coordinate with Emergency Medical cally ill patients.
Section01.indd 61 1/22/2015 9:37:07 AM