Page 16 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 16
Plate 1-1 Integumentary System
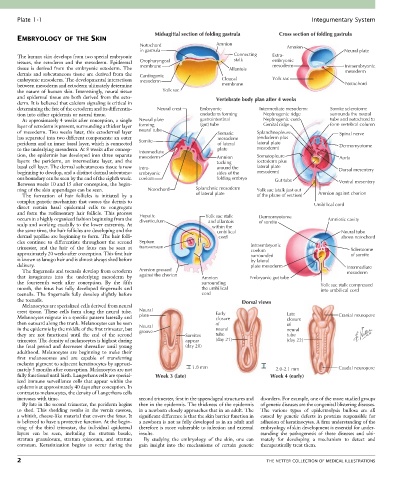
Midsagittal section of folding gastrula Cross section of folding gastrula
EMBRYOLOGY OF THE SKIN
Notochord Amnion Amnion
in gastrula Neural plate
The human skin develops from two special embryonic Connecting Extra-
tissues, the ectoderm and the mesoderm. Epidermal Oropharyngeal stalk embryonic
tissue is derived from the embryonic ectoderm. The membrane Allantois mesoderm Intraembryonic
dermis and subcutaneous tissue are derived from the Cardiogenic mesoderm
embryonic mesoderm. The developmental interactions mesoderm Cloacal Yolk sac
between mesoderm and ectoderm ultimately determine membrane Notochord
the nature of human skin. Interestingly, neural tissue Yolk sac
and epidermal tissue are both derived from the ecto- Vertebrate body plan after 4 weeks
derm. It is believed that calcium signaling is critical in
determining the fate of the ectoderm and its differentia- Neural crest Embryonic Intermediate mesoderm: Somite sclerotome
tion into either epidermis or neural tissue. endoderm forming Nephrogenic ridge surrounds the neural
At approximately 4 weeks after conception, a single Neural plate gastrointestinal Nephrogenic cord tube and notochord to
layer of ectoderm is present, surrounding a thicker layer forming (gut) tube Genital ridge form vertebral column
of mesoderm. Two weeks later, this ectodermal layer neural tube Somatic Splanchnopleure Spinal nerve
has separated into two different components: an outer mesoderm (endoderm plus
periderm and an inner basal layer, which is connected Somite of lateral lateral plate Dermomyotome
to the underlying mesoderm. At 8 weeks after concep- Intermediate plate mesoderm)
tion, the epidermis has developed into three separate mesoderm Amnion Somatopleure Aorta
layers: the periderm, an intermediate layer, and the tucking (ectoderm plus
basal cell layer. The dermal subcutaneous tissue is now Intra- around the lateral plate
beginning to develop, and a distinct dermal subcutane- embryonic sides of the mesoderm) Dorsal mesentery
ous boundary can be seen by the end of the eighth week. coelom folding embryo Gut tube
Between weeks 10 and 15 after conception, the begin- Ventral mesentery
ning of the skin appendages can be seen. Notochord Splanchnic mesoderm Yolk sac (stalk just out
The formation of hair follicles is initiated by a of lateral plate of the plane of section) Amnion against chorion
complex genetic mechanism that causes the dermis to
direct certain basal epidermal cells to congregate Umbilical cord
and form the rudimentary hair follicle. This process
occurs in a highly organized fashion beginning from the Hepatic Yolk sac stalk Dermomyotome Amniotic cavity
diverticulum
and allantois
scalp and working caudally to the lower extremity. At within the of somite
the same time, the hair follicles are developing and the umbilical Neural tube
dermal papillae are beginning to form. The hair folli- cord above notochord
cles continue to differentiate throughout the second Septum
trimester, and the hair of the fetus can be seen at transversum Intraembryonic Sclerotome
coelom
approximately 20 weeks after conception. This first hair surrounded of somite
is known as lanugo hair and is almost always shed before by lateral
delivery. plate mesoderm Intermediate
The fingernails and toenails develop from ectoderm Amnion pressed mesoderm
that invaginates into the underlying mesoderm by against the chorion Amnion Embryonic gut tube
the fourteenth week after conception. By the fifth surrounding Yolk sac stalk compressed
month, the fetus has fully developed fingernails and the umbilical into umbilical cord
toenails. The fingernails fully develop slightly before cord
the toenails. Dorsal views
Melanocytes are specialized cells derived from neural
crest tissue. These cells form along the neural tube. Neural Early Late
Melanocytes migrate in a specific pattern laterally and plate closure closure Cranial neuropore
then outward along the trunk. Melanocytes can be seen of of
in the epidermis by the middle of the first trimester, but Neural neural neural
groove
they are not functional until the end of the second Somites tube tube
trimester. The density of melanocytes is highest during appear (day 21) (day 22)
the fetal period and decreases thereafter until young (day 20)
adulthood. Melanocytes are beginning to make their
first melanosomes and are capable of transferring
melanin pigment to adjacent keratinocytes by approxi-
mately 5 months after conception. Melanocytes are not 1.8 mm 2.0-2.1 mm Caudal neuropore
fully functional until birth. Langerhans cells are special- Week 3 (late) Week 4 (early)
ized immune surveillance cells that appear within the
epidermis at approximately 40 days after conception. In
contrast to melanocytes, the density of Langerhans cells
increases with time. second trimester, first in the appendageal structures and disorders. For example, one of the more studied groups
By late in the second trimester, the periderm begins then in the epidermis. The thickness of the epidermis of genetic diseases are the congenital blistering diseases.
to shed. This shedding results in the vernix caseosa, in a newborn closely approaches that in an adult. The The various types of epidermolysis bullosa are all
a whitish, cheese-like material that covers the fetus. It significant difference is that the skin barrier function in caused by genetic defects in proteins responsible for
is believed to have a protective function. At the begin- a newborn is not as fully developed as in an adult and adhesion of keratinocytes. A firm understanding of the
ning of the third trimester, the individual epidermal therefore is more vulnerable to infection and external embryology of skin development is essential for under-
layers can be seen, including the stratum basale, insults. standing the pathogenesis of these diseases and ulti-
stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum By studying the embryology of the skin, one can mately for developing a mechanism to detect and
corneum. Keratinization begins to occur during the gain insight into the mechanisms of certain genetic therapeutically treat them.
2 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS