Page 18 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 18
Plate 1-3 Integumentary System
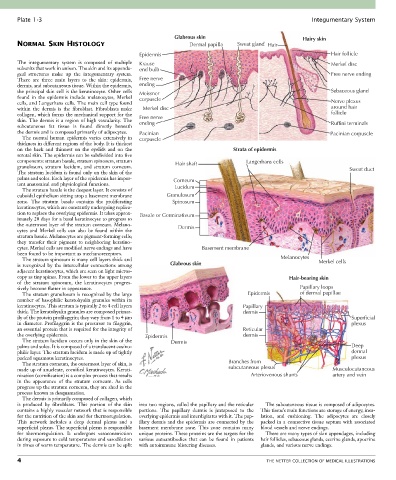
Glabrous skin Hairy skin
NORMAL SKIN HISTOLOGY Dermal papilla Sweat gland Hair
Epidermis Hair follicle
The integumentary system is composed of multiple Krause Merkel disc
subunits that work in unison. The skin and its appenda- end bulb
geal structures make up the integumentary system. Free nerve ending
There are three main layers to the skin: epidermis, Free nerve
dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Within the epidermis, ending
the principal skin cell is the keratinocyte. Other cells Meissner Sebaceous gland
found in the epidermis include melanocytes, Merkel corpuscle
cells, and Langerhans cells. The main cell type found Nerve plexus
within the dermis is the fibroblast. Fibroblasts make Merkel disc around hair
collagen, which forms the mechanical support for the Free nerve follicle
skin. The dermis is a region of high vascularity. The ending Ruffini terminals
subcutaneous fat tissue is found directly beneath
the dermis and is composed primarily of adipocytes. Pacinian Pacinian corpuscle
The normal human epidermis varies extensively in corpuscle
thickness in different regions of the body. It is thickest
on the back and thinnest on the eyelids and on the Strata of epidermis
scrotal skin. The epidermis can be subdivided into five
components: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum Hair shaft Langerhans cells
granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. Sweat duct
The stratum lucidum is found only on the skin of the
palms and soles. Each layer of the epidermis has impor- Corneum
tant anatomical and physiological functions. Lucidum
The stratum basale is the deepest layer. It consists of
cuboidal epithelium sitting atop a basement membrane Granulosum
zone. The stratum basale contains the proliferating Spinosum
keratinocytes, which are constantly undergoing replica-
tion to replace the overlying epidermis. It takes approx- Basale or Germinativum
imately 28 days for a basal keratinocyte to progress to
the outermost layer of the stratum corneum. Melano- Dermis
cytes and Merkel cells can also be found within the
stratum basale. Melanocytes are pigment-forming cells;
they transfer their pigment to neighboring keratino-
cytes. Merkel cells are modified nerve endings and have Basement membrane
been found to be important as mechanoreceptors.
The stratum spinosum is many cell layers thick and Melanocytes Merkel cells
is recognized by the intercellular connections among Glabrous skin
adjacent keratinocytes, which are seen on light micros-
copy as tiny spines. From the lower to the upper layers Hair-bearing skin
of the stratum spinosum, the keratinocytes progres-
sively become flatter in appearance. Papillary loops
The stratum granulosum is recognized by the large Epidermis of dermal papillae
number of basophilic keratohyalin granules within its
keratinocytes. This stratum is typically 2 to 4 cell layers Papillary
thick. The keratohyalin granules are composed primar- dermis
ily of the protein profilaggrin; they vary from 1 to 4 µm Superficial
in diameter. Profilaggrin is the precursor to filaggrin, plexus
an essential protein that is required for the integrity of Reticular
the overlying epidermis. Epidermis dermis
The stratum lucidum occurs only in the skin of the Dermis
palms and soles. It is composed of a translucent eosino- Deep
philic layer. The stratum lucidum is made up of tightly dermal
packed squamous keratinocytes. plexus
The stratum corneum, the outermost layer of skin, is Branches from
made up of anucleate, cornified keratinocytes. Kerati- subcutaneous plexus Musculocutaneous
nization (cornification) is a complex process that results Arteriovenous shunts artery and vein
in the appearance of the stratum corneum. As cells
progress up the stratum corneum, they are shed in the
process known as desquamation.
The dermis is primarily composed of collagen, which
is produced by fibroblasts. This portion of the skin into two regions, called the papillary and the reticular The subcutaneous tissue is composed of adipocytes.
contains a highly vascular network that is responsible portions. The papillary dermis is juxtaposed to the This tissue’s main functions are storage of energy, insu-
for the nutrition of the skin and for thermoregulation. overlying epidermis and interdigitates with it. The pap- lation, and cushioning. The adipocytes are closely
This network includes a deep dermal plexus and a illary dermis and the epidermis are connected by the packed in a connective tissue septum with associated
superficial plexus. The superficial plexus is responsible basement membrane zone. This zone contains many blood vessels and nerve endings.
for thermoregulation. It undergoes vasoconstriction unique proteins. These proteins are the targets for the There are many types of skin appendages, including
during exposure to cold temperatures and vasodilation various autoantibodies that can be found in patients hair follicles, sebaceous glands, eccrine glands, apocrine
in times of warm temperature. The dermis can be split with autoimmune blistering diseases. glands, and various nerve endings.
4 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS