Page 20 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 20
Plate 1-5 Integumentary System
NORMAL SKIN FLORA
The skin contains normal microflora that are universally
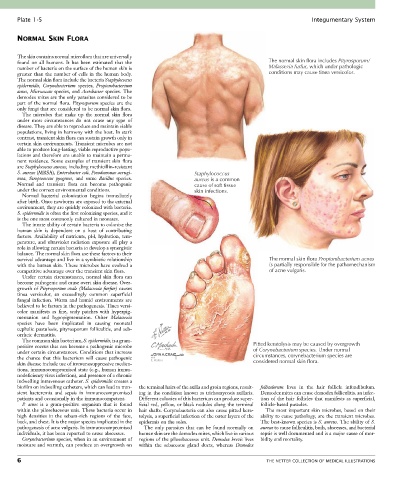
found on all humans. It has been estimated that the The normal skin flora includes Pityrosporum/
number of bacteria on the surface of the human skin is Malassezia furfur, which under pathologic
greater than the number of cells in the human body. conditions may cause tinea versicolor.
The normal skin flora include the bacteria Staphylococcus
epidermidis, Corynebacterium species, Propionobacterium
acnes, Micrococcus species, and Acetobacter species. The
demodex mites are the only parasites considered to be
part of the normal flora. Pityrosporum species are the
only fungi that are considered to be normal skin flora.
The microbes that make up the normal skin flora
under most circumstances do not cause any type of
disease. They are able to reproduce and maintain viable
populations, living in harmony with the host. In stark
contrast, transient skin flora can sustain growth only in
certain skin environments. Transient microbes are not
able to produce long-lasting, viable reproductive popu-
lations and therefore are unable to maintain a perma-
nent residence. Some examples of transient skin flora
are Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant
S. aureus (MRSA), Enterobacter coli, Pseudomonas aerugi- Staphylococcus
nosa, Streptococcus pyogenes, and some Bacillus species. aureus is a common
Normal and transient flora can become pathogenic cause of soft tissue
under the correct environmental conditions. skin infections.
Normal bacterial colonization begins immediately
after birth. Once newborns are exposed to the external
environment, they are quickly colonized with bacteria.
S. epidermidis is often the first colonizing species, and it
is the one most commonly cultured in neonates.
The innate ability of certain bacteria to colonize the
human skin is dependent on a host of contributing
factors. Availability of nutrients, pH, hydration, tem-
perature, and ultraviolet radiation exposure all play a
role in allowing certain bacteria to develop a synergistic
balance. The normal skin flora use these factors to their
survival advantage and live in a symbiotic relationship The normal skin flora Propionibacterium acnes
with the human skin. These microbes have evolved a is partially responsible for the pathomechanism
competitive advantage over the transient skin flora. of acne vulgaris.
Under certain circumstances, normal skin flora can
become pathogenic and cause overt skin disease. Over-
growth of Pityrosporum ovale (Malassezia furfur) causes
tinea versicolor, an exceedingly common superficial
fungal infection. Warm and humid environments are
believed to be factors in the pathogenesis. Tinea versi-
color manifests as fine, scaly patches with hyperpig-
mentation and hypopigmentation. Other Malassezia
species have been implicated in causing neonatal
cephalic pustulosis, pityrosporum folliculitis, and seb-
orrheic dermatitis.
The common skin bacterium, S. epidermidis, is a gram-
positive coccus that can become a pathogenic microbe Pitted keratolysis may be caused by overgrowth
under certain circumstances. Conditions that increase of Corynebacterium species. Under normal
the chance that this bacterium will cause pathogenic with circumstances, corynebacterium species are
E. Hatton
skin disease include use of immunosuppressive medica- considered normal skin flora.
tions, immunocompromised state (e.g., human immu-
nodeficiency virus infection), and presence of a chronic
indwelling intravenous catheter. S. epidermidis creates a
biofilm on indwelling catheters, which can lead to tran- the terminal hairs of the axilla and groin regions, result- folliculorum lives in the hair follicle infundibulum.
sient bacteremia and sepsis in immunocompromised ing in the condition known as trichomycosis axillaris. Demodex mites can cause demodex folliculitis. an infec-
patients and occasionally in the immunocompetent. Different colonies of this bacterium can produce super- tion of the hair follicles that manifests as superficial,
P. acnes is a gram-positive organism that is found ficial red, yellow, or black nodules along the terminal follicle-based pustules.
within the pilosebaceous unit. These bacteria occur in hair shafts. Corynebacteria can also cause pitted kera- The most important skin microbes, based on their
high densities in the sebum-rich regions of the face, tolysis, a superficial infection of the outer layers of the ability to cause pathology, are the transient microbes.
back, and chest. It is the major species implicated in the epidermis on the soles. The best-known species is S. aureus. The ability of S.
pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. In immunocompromised The only parasites that can be found normally on aureus to cause folliculitis, boils, abscesses, and bacterial
individuals, it has been reported to cause abscesses. human skin are the demodex mites, which live in various sepsis is well documented and is a major cause of mor-
Corynebacterium species, when in an environment of regions of the pilosebaceous unit. Demodex brevis lives bidity and mortality.
moisture and warmth, can produce an overgrowth on within the sebaceous gland ducts, whereas Demodex
6 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS