Page 17 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 17
Plate 1-2 Anatomy, Physiology, and Embryology
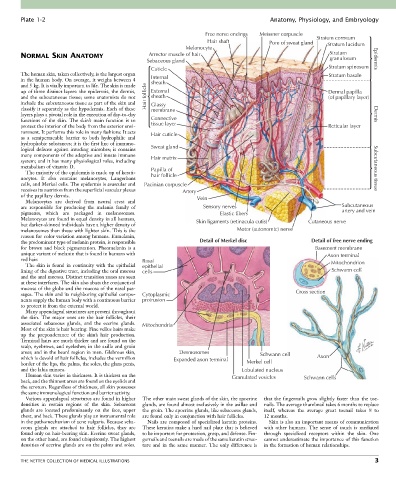
Free nerve endings Meissner corpuscle Stratum corneum
Hair shaft Pore of sweat gland Stratum lucidum
Melanocyte
NORMAL SKIN ANATOMY Arrector muscle of hair Stratum
granulosum
Sebaceous gland Epidermis
Cuticle Stratum spinosum
The human skin, taken collectively, is the largest organ Stratum basale
in the human body. On average, it weighs between 4 Internal
sheath
and 5 kg. It is vitally important to life. The skin is made
up of three distinct layers: the epidermis, the dermis, External Dermal papilla
and the subcutaneous tissue; some anatomists do not Hair follicle sheath (of papillary layer)
include the subcutaneous tissue as part of the skin and Glassy
classify it separately as the hypodermis. Each of these membrane
layers plays a pivotal role in the execution of day-to-day Dermis
functions of the skin. The skin’s main function is to Connective
protect the interior of the body from the exterior envi- tissue layer Reticular layer
ronment. It performs this role in many fashions: It acts Hair cuticle
as a semipermeable barrier to both hydrophilic and
hydrophobic substances; it is the first line of immuno-
logical defense against invading microbes; it contains Sweat gland
many components of the adaptive and innate immune Hair matrix
system; and it has many physiological roles, including
metabolism of vitamin D. Papilla of Subcutaneous tissue
The majority of the epidermis is made up of kerati-
nocytes. It also contains melanocytes, Langerhans hair follicle
cells, and Merkel cells. The epidermis is avascular and Pacinian corpuscle
receives its nutrition from the superficial vascular plexus Artery
of the papillary dermis. Vein
Melanocytes are derived from neural crest and
are responsible for producing the melanin family of Sensory nerves Subcutaneous
pigments, which are packaged in melanosomes. Elastic fibers artery and vein
Melanocytes are found in equal density in all humans, Skin ligaments (retinacula cutis) Cutaneous nerve
but darker-skinned individuals have a higher density of
melanosomes than those with lighter skin. This is the Motor (autonomic) nerve
reason for color variation among humans. Eumelanin,
the predominant type of melanin protein, is responsible Detail of Merkel disc Detail of free nerve ending
for brown and black pigmentation. Pheomelanin is a Basement membrane
unique variant of melanin that is found in humans with Axon terminal
red hair. Basal
The skin is found in continuity with the epithelial epithelial Mitochondrion
lining of the digestive tract, including the oral mucosa cells Schwann cell
and the anal mucosa. Distinct transition zones are seen
at these interfaces. The skin also abuts the conjunctival
mucosa of the globe and the mucosa of the nasal pas-
sages. The skin and its neighboring epithelial compo- Cytoplasmic Cross section
nents supply the human body with a continuous barrier protrusion
to protect it from the external world.
Many appendageal structures are present throughout
the skin. The major ones are the hair follicles, their
associated sebaceous glands, and the eccrine glands. Mitochondria
Most of the skin is hair bearing. Fine vellus hairs make
up the preponderance of the skin’s hair production.
Terminal hairs are much thicker and are found on the
scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes; in the axilla and groin
areas; and in the beard region in men. Glabrous skin, Desmosomes Schwann cell
which is devoid of hair follicles, includes the vermilion Expanded axon terminal Axon
border of the lips, the palms, the soles, the glans penis, Merkel cell
and the labia minora. Lobulated nucleus
Human skin varies in thickness. It is thickest on the Granulated vesicles Schwann cells
back, and the thinnest areas are found on the eyelids and
the scrotum. Regardless of thickness, all skin possesses
the same immunological function and barrier activity.
Various appendageal structures are found in higher The other main sweat glands of the skin, the apocrine that the fingernails grow slightly faster than the toe-
densities in certain regions of the skin. Sebaceous glands, are found almost exclusively in the axillae and nails. The average thumbnail takes 6 months to replace
glands are located predominantly on the face, upper the groin. The apocrine glands, like sebaceous glands, itself, whereas the average great toenail takes 8 to
chest, and back. These glands play an instrumental role are found only in conjunction with hair follicles. 12 months.
in the pathomechanism of acne vulgaris. Because seba- Nails are composed of specialized keratin proteins. Skin is also an important means of communication
ceous glands are attached to hair follicles, they are These keratins make a hard nail plate that is believed with other humans. The sense of touch is mediated
found only on hair-bearing skin. Eccrine sweat glands, to be important for protection, grasp, and defense. Fin- through specialized receptors within the skin. One
on the other hand, are found ubiquitously. The highest gernails and toenails are made of the same keratin struc- cannot underestimate the importance of this function
densities of eccrine glands are on the palms and soles. ture and in the same manner. The only difference is in the formation of human relationships.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 3