Page 21 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 21
Plate 1-6 Anatomy, Physiology, and Embryology
NORMAL CALCIUM AND PHOSPHATE METABOLISM
++
Ca and PO 4 Sun Parathyroid
VITAMIN D METABOLISM in food Vit. D 2 3 Ultraviolet light hormone (PTH)
Vit. D
(UVB)
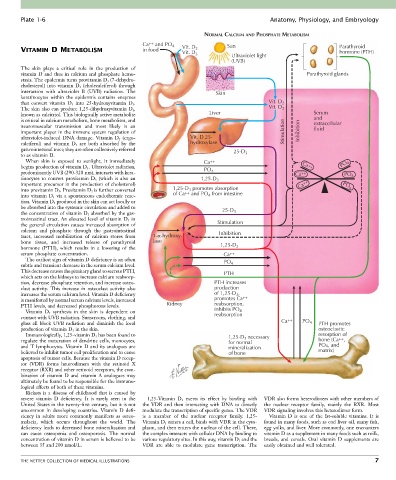
The skin plays a critical role in the production of
vitamin D and thus in calcium and phosphate hemo- Parathyroid glands
stasis. The epidermis turns provitamin D 3 (7-dehydro-
cholesterol) into vitamin D 3 (cholecalciferol) through
interaction with ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation. The Skin
keratinocytes within the epidermis contains enzymes
that convert vitamin D 3 into 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 . Vit. D 2
The skin also can produce 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 , Vit. D 3
known as calcitriol. This biologically active metabolite Liver Serum
is critical in calcium metabolism, bone metabolism, and and
extracellular
neuromuscular transmission and most likely is an fluid
important player in the immune system regulation of Stimulation Inhibition
ultraviolet-induced DNA damage. Vitamin D 2 (ergo- Vit. D 25-
calciferol) and vitamin D 3 are both absorbed by the hydroxylase
gastrointestinal tract; they are often collectively referred 25-D
to as vitamin D. 3
When skin is exposed to sunlight, it immediately Ca ++
begins production of vitamin D 3 . Ultraviolet radiation, PO Ca ++ PO 4
predominantly UVB (290-320 nm), interacts with kera- 4 Ca ++ PO
tinocytes to convert provitamin D 3 (which is also an 1,25-D 3 4
important precursor in the production of cholesterol) Ca ++ PO 4
into previtamin D 3 . Previtamin D 3 is further converted 1,25-D promotes absorption
3
4
into vitamin D 3 via a spontaneous endothermic reac- of Ca ++ and PO from intestine
tion. Vitamin D 3 produced in the skin can act locally or
be absorbed into the systemic circulation and added to 25-D
the concentration of vitamin D 3 absorbed by the gas- 3
trointestinal tract. An elevated level of vitamin D 3 in
the general circulation causes increased absorption of Stimulation
calcium and phosphate through the gastrointestinal Inhibition
tract, increased mobilization of calcium stores from 1- -hydroxy-
bone tissue, and increased release of parathyroid lase 1,25-D
hormone (PTH), which results in a lowering of the 3
serum phosphate concentration. Ca ++
The earliest sign of vitamin D deficiency is an often PO
subtle and transient decrease in the serum calcium level. 4
This decrease causes the pituitary gland to secrete PTH, PTH
which acts on the kidneys to increase calcium reabsorp-
tion, decrease phosphate retention, and increase osteo- PTH increases
clast activity. This increase in osteoclast activity also production
increases the serum calcium level. Vitamin D deficiency of 1,25-D 3 ,
is manifested by normal serum calcium levels, increased promotes Ca ++
PTH levels, and decreased phosphorous levels. Kidney reabsorption,
Vitamin D 3 synthesis in the skin is dependent on inhibits PO 4
contact with UVB radiation. Sunscreens, clothing, and reabsorption
glass all block UVB radiation and diminish the local Ca ++ PO 4 PTH promotes
production of vitamin D 3 in the skin. osteoclastic
Immunologically, 1,25-vitamin D 3 has been found to 1,25-D necessary resorption of
3
regulate the maturation of dendritic cells, monocytes, for normal bone (Ca ++ ,
and T lymphocytes. Vitamin D and its analogues are mineralization PO4, and
believed to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and to cause of bone matrix)
apoptosis of tumor cells. Because the vitamin D recep-
tor (VDR) forms heterodimers with the retinoid X
receptor (RXR) and other retinoid receptors, the com-
bination of vitamin D and vitamin A analogues may
ultimately be found to be responsible for the immuno-
logical effects of both of these vitamins.
Rickets is a disease of childhood that is caused by
severe vitamin D deficiency. It is rarely seen in the 1,25-Vitamin D 3 exerts its effect by binding with VDR also forms heterodimers with other members of
United States in the twenty-first century, but it is not the VDR and then interacting with DNA to directly the nuclear receptor family, mainly the RXR. Most
uncommon in developing countries. Vitamin D defi- modulate the transcription of specific genes. The VDR VDR signaling involves this heterodimer form.
ciency in adults more commonly manifests as osteo- is a member of the nuclear receptor family. 1,25- Vitamin D is one of the fat-soluble vitamins. It is
malacia, which occurs throughout the world. The Vitamin D 3 enters a cell, binds with VDR in the cyto- found in many foods, such as cod liver oil, many fish,
deficiency leads to decreased bone mineralization and plasm, and then enters the nucleus of the cell. There, egg yolks, and liver. More commonly, one encounters
can cause osteopenia and osteoporosis. The normal the complex interacts with cellular DNA by binding to vitamin D as a supplement in many foods such as milk,
concentration of vitamin D in serum is believed to be various regulatory sites. In this way, vitamin D 3 and the breads, and cereals. Oral vitamin D supplements are
between 35 and 200 nmol/L. VDR are able to modulate gene transcription. The easily obtained and well tolerated.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 7