Page 312 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 312
278 Chapter 10
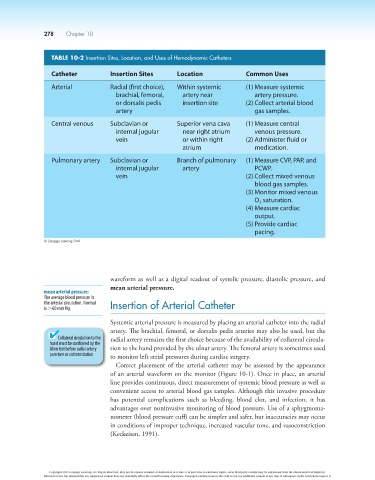
TABLE 10-2 Insertion Sites, Location, and Uses of Hemodynamic Catheters
Catheter Insertion Sites Location Common Uses
Arterial Radial (first choice), Within systemic (1) Measure systemic
brachial, femoral, artery near artery pressure.
or dorsalis pedis insertion site (2) Collect arterial blood
artery gas samples.
Central venous Subclavian or Superior vena cava (1) Measure central
internal jugular near right atrium venous pressure.
vein or within right (2) Administer fluid or
atrium medication.
Pulmonary artery Subclavian or Branch of pulmonary (1) Measure CVP, PAP, and
internal jugular artery PCWP.
vein (2) Collect mixed venous
blood gas samples.
(3) Monitor mixed venous
O saturation.
2
(4) Measure cardiac
output.
(5) Provide cardiac
pacing.
© Cengage Learning 2014
waveform as well as a digital readout of systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, and
mean arterial pressure.
mean arterial pressure:
The average blood pressure in
the arterial circulation. Normal Insertion of Arterial Catheter
is .60 mm Hg.
Systemic arterial pressure is measured by placing an arterial catheter into the radial
artery. The brachial, femoral, or dorsalis pedis arteries may also be used, but the
Collateral circulation to the radial artery remains the first choice because of the availability of collateral circula-
hand must be confirmed by the
Allen test before radial artery tion to the hand provided by the ulnar artery. The femoral artery is sometimes used
puncture or catheterization. to monitor left atrial pressures during cardiac surgery.
Correct placement of the arterial catheter may be assessed by the appearance
of an arterial waveform on the monitor (Figure 10-1). Once in place, an arterial
line provides continuous, direct measurement of systemic blood pressure as well as
convenient access to arterial blood gas samples. Although this invasive procedure
has potential complications such as bleeding, blood clot, and infection, it has
advantages over noninvasive monitoring of blood pressure. Use of a sphygmoma-
nometer (blood pressure cuff) can be simpler and safer, but inaccuracies may occur
in conditions of improper technique, increased vascular tone, and vasoconstriction
(Keckeisen, 1991).
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.