Page 414 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 414
380 Chapter 12
STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE OXYGENATION
Oxygenation is dependent on adequate and well-balanced ventilation, diffusion,
oxygenation: Amount of oxygen
available for metabolic functions; and perfusion. The strategies to improve oxygenation are therefore structured to
affected by ventilation, diffusion improve the normal physiologic functions or to compensate for the abnormal ones.
and perfusion.
The prioritized methods to improve oxygenation, from simple to complex, are
outlined in Table 12-3.
Increase Inspired Oxygen Fraction (F O )
I
2
Supplemental oxygen is most frequently used to manage hypoxemia because a high
Oxygen readily corrects F O increases the alveolar-capillary oxygen pressure gradient, thus enhancing dif-
hypoxemia that is due to I 2
uncomplicated V/Q mismatch. fusion of oxygen from the lungs to the pulmonary circulation. Oxygen readily
corrects hypoxemia that is due to uncomplicated V/Q mismatch.
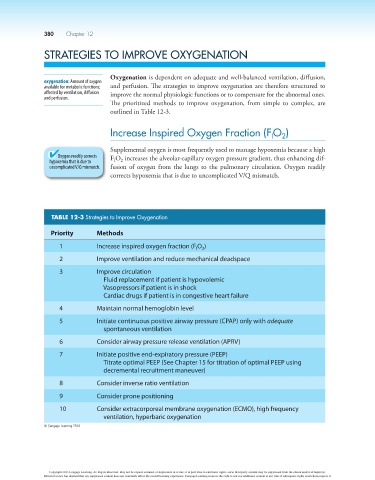
TABLE 12-3 Strategies to Improve Oxygenation
Priority Methods
1 Increase inspired oxygen fraction (F O )
I
2
2 Improve ventilation and reduce mechanical deadspace
3 Improve circulation
Fluid replacement if patient is hypovolemic
Vasopressors if patient is in shock
Cardiac drugs if patient is in congestive heart failure
4 Maintain normal hemoglobin level
5 Initiate continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) only with adequate
spontaneous ventilation
6 Consider airway pressure release ventilation (APRV)
7 Initiate positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
Titrate optimal PEEP (See Chapter 15 for titration of optimal PEEP using
decremental recruitment maneuver)
8 Consider inverse ratio ventilation
9 Consider prone positioning
10 Consider extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), high frequency
ventilation, hyperbaric oxygenation
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.