Page 418 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 418
384 Chapter 12
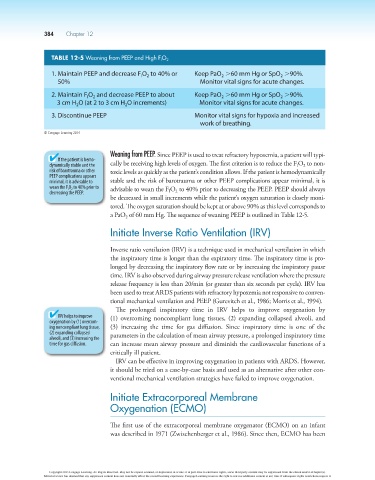
TABLE 12-5 Weaning from PEEP and High F I O 2
1. Maintain PEEP and decrease F O to 40% or Keep PaO .60 mm Hg or SpO .90%.
2
2
2
I
50% Monitor vital signs for acute changes.
2. Maintain F O and decrease PEEP to about Keep PaO .60 mm Hg or SpO .90%.
2
2
I
2
3 cm H O (at 2 to 3 cm H O increments) Monitor vital signs for acute changes.
2
2
3. Discontinue PEEP Monitor vital signs for hypoxia and increased
work of breathing.
© Cengage Learning 2014
Weaning from PEEP. Since PEEP is used to treat refractory hypoxemia, a patient will typi-
If the patient is hemo-
dynamically stable and the cally be receiving high levels of oxygen. The first criterion is to reduce the F O to non-
I
2
risk of barotrauma or other toxic levels as quickly as the patient’s condition allows. If the patient is hemodynamically
PEEP complications appears
minimal, it is advisable to stable and the risk of barotrauma or other PEEP complications appear minimal, it is
wean the F I O 2 to 40% prior to advisable to wean the F O to 40% prior to decreasing the PEEP. PEEP should always
decreasing the PEEP. I 2
be decreased in small increments while the patient’s oxygen saturation is closely moni-
tored. The oxygen saturation should be kept at or above 90% as this level corresponds to
a PaO of 60 mm Hg. The sequence of weaning PEEP is outlined in Table 12-5.
2
Initiate Inverse Ratio Ventilation (IRV)
Inverse ratio ventilation (IRV) is a technique used in mechanical ventilation in which
the inspiratory time is longer than the expiratory time. The inspiratory time is pro-
longed by decreasing the inspiratory flow rate or by increasing the inspiratory pause
time. IRV is also observed during airway pressure release ventilation where the pressure
release frequency is less than 20/min (or greater than six seconds per cycle). IRV has
been used to treat ARDS patients with refractory hypoxemia not responsive to conven-
tional mechanical ventilation and PEEP (Gurevitch et al., 1986; Morris et al., 1994).
The prolonged inspiratory time in IRV helps to improve oxygenation by
IRV helps to improve (1) overcoming noncompliant lung tissues, (2) expanding collapsed alveoli, and
oxygenation by (1) overcom-
ing noncompliant lung tissue, (3) increasing the time for gas diffusion. Since inspiratory time is one of the
(2) expanding collapsed parameters in the calculation of mean airway pressure, a prolonged inspiratory time
alveoli, and (3) increasing the
time for gas diffusion. can increase mean airway pressure and diminish the cardiovascular functions of a
critically ill patient.
IRV can be effective in improving oxygenation in patients with ARDS. However,
it should be tried on a case-by-case basis and used as an alternative after other con-
ventional mechanical ventilation strategies have failed to improve oxygenation.
Initiate Extracorporeal Membrane
Oxygenation (ECMO)
The first use of the extracorporeal membrane oxygenator (ECMO) on an infant
was described in 1971 (Zwischenberger et al., 1986). Since then, ECMO has been
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.