Page 460 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 460
426 Chapter 13
Special Considerations. The primary purpose of beta agonists is bronchodilation. For
patients with inflammatory airway disease (i.e., asthma and chronic bronchitis),
intermittent use of beta agonists may not be sufficient. Deaths have been reported
in asthmatics following regular and prolonged use of these agents. Uncontrolled
inflammation and mucosal edema are likely the cause of this adverse outcome
(Witek, 1994).
Desensitization of receptor sites has been documented with regular use of beta
agonists. Two mechanisms appear to be responsible: (1) the loss of receptor from
the surface of cells and (2) the failure of the cell to function (Cottrell et al., 1995).
The practitioner may wish to combine beta agonists with other categories of drugs
to achieve bronchodilation. For example, a combination of corticosteroid and beta
agonist may potentiate their individual effects and produce bronchodilation.
However, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur with combined use of adrenergic
agonists and corticosteroids. Its occurrence is rare, but the onset can be sudden. For
this reason, practitioners should be aware of the hazard.
Anticholinergic Bronchodilators
acetylcholine: An ester that
plays a role in the transmission (Parasympatholytics)
of nerve impulses at synapses
and neuromuscular junctions.
It is metabolized by an enzyme, Anticholinergic bronchodilators are agents that impede the impulses of the cholin-
cholinesterase. Too much or too
little of acetylcholine at the motor ergic, especially the parasympathetic nerve fibers of the autonomic nervous system.
endplates may lead to muscle
blockade. Mechanism of Action. Parasympathetic receptors (muscarinic and nicotinic) are
found throughout the body. They are classified according to whether they respond
to muscarine or nicotine. In the lungs, muscarinic receptors are found in submuco-
Atropine is an anti- sal glands, mast cells, and smooth muscles of the larger airways.
cholinergic agent used as a The combination of acetylcholine with muscarinic receptors results in increased
secondary bronchodilator. It
is also used for symptomatic bronchial tone and increased secretion from mucosal glands. Anticholinergic agents
bradycardia and prophylactic (atropine and atropine derivatives) block these physiologic responses and may be
drying of secretions before
surgery. useful for the reversal of vagally mediated bronchospasm. Table 13-4 shows the
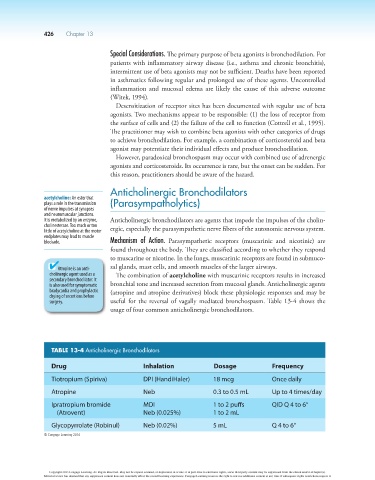
usage of four common anticholinergic bronchodilators.
TABLE 13-4 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators
Drug Inhalation Dosage Frequency
Tiotropium (Spiriva) DPI (HandiHaler) 18 mcg Once daily
Atropine Neb 0.3 to 0.5 mL Up to 4 times/day
Ipratropium bromide MDI 1 to 2 puffs QID Q 4 to 6°
(Atrovent) Neb (0.025%) 1 to 2 mL
Glycopyrrolate (Robinul) Neb (0.02%) 5 mL Q 4 to 6°
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.